Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits
Exercise : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 2
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 5
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 6
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 7
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 8
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 10
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 12
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 13
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 14
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 15
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 16
36.
Secondary emission is always decremental.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Sometimes it can be useful also.
37.
In a degenerate n type semiconductor material, the Fermi level,
Answer: Option
Explanation:
This is due to high level of doping.
38.
The types of carriers in a semiconductor are
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Holes and electrons.
39.
A potential of 7 V is applied to a silicon diode. A resistance of 1 K ohm is also in series with the diode. The current is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
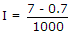
40.
Assertion (A): The reverse saturation current in a semiconductor diode is 4nA at 20°C and 32 nA at 50°C.
Reason (R): The reverse saturation current in a semiconductor diode doubles for every 10°C rise in temperature.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
At 20°C, 4 nA, at 30°C, 8 nA, at 40°C, 16 nA, at 50°C, 32 nA.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers