Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits
Exercise : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 2
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 5
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 6
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 7
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 8
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 10
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 12
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 13
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 14
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 15
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 16
21.
When a diode is not conducting, its bias is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Diode conducts only when forward biased. There is no conduction when bias is zero or reverse.
22.
The SCR would be turned OFF by voltage reversal of applied anode-cathode ac supply of frequency of
Answer: Option
Explanation:
For inverter grade SCR, typical turn off time (toff) is 5 to 50 μsec while 50 to 100 μsec for converter grade SCR.
Hence supply frequency of 5 kHz will turn off the SCR by voltage reversal
because 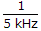 = 200 μsec.
= 200 μsec.
23.
The number of valence electrons in a donor atom is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Therefore, it can donate one electron.
24.
An electron rises through a voltage of 100 V. The energy acquired by it will be
Answer: Option
Explanation:
When an electron rises through 1 V, energy = 1 eV.
25.
Measurement of hall coefficient enables the determination of
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Hall effect can be used to find type and concentration of charge carriers.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers