Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test 8
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
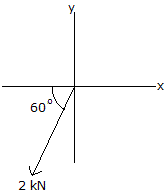
Determine the magnitude of the x and y components of the 2—kN force.
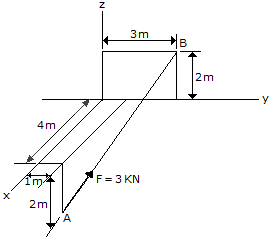
Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then determine its direction angles.
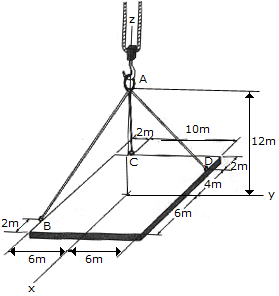
The ends of the three cables are attached to ring at A and to the edge of a uniform 150-kg plate. Determine the tension in each of the cables for equilibrium.

Determine the moment of the force at A about point P. Use a vector analysis and express the result in Cartesian vector form.

A force of 50 N is applied to the handle of the door as shown. Determine the projection of the moment of this force about the hinged axis z. Neglect the size of the doorknob. Suggestion: Use a scaler analysis.
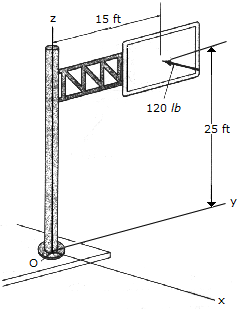
The resultant force of a wind loading acts perpendicular to the face of the sign as shown. Replace this force by an equivalent force and couple moment acting at point O.
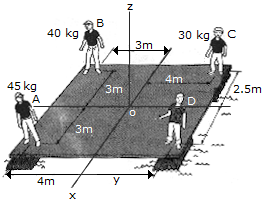
The boys A, B and C stand near the edges of a raft as shown. Determine the location (x, y) of boy D so that all four boys create a single resultant force acting through the raft's center O. Provided the raft itself is symmetric, this would keep the raft afloat in a horizontal plane. the mass of each boy is indicated in the diagram.
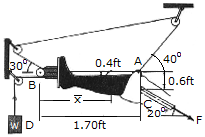
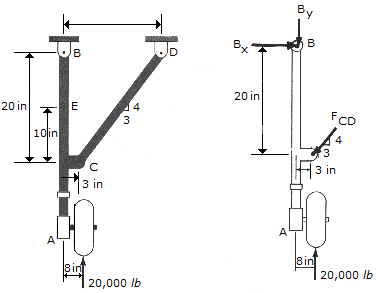
A Russell's traction is used for immobilizing femoral fractures C. If the lower leg has a weight of 8 lb, determine the weight W that must be suspended at D in order for the leg to be held in the position shown. Also, what is the tension force F in the femur and the distance 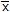 which locates the center of gravity G of the lower leg? Neglect the size of the pulley at B.
which locates the center of gravity G of the lower leg? Neglect the size of the pulley at B.
There is a ball and socket connection at A. At point B there is a connection that opposes motion in the x and z directions only. Determine the unknown force components at A and B. Use a scalar analysis.
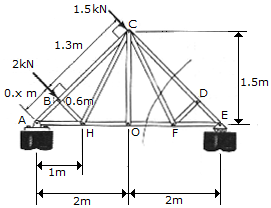
Determine the force in members GF, CF, CD of the symmetric roof truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression.
Determine the internal axial force, shear force, and moment at point E of the oleo strut AB of the aircraft landing gear.
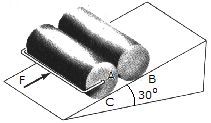
Determine the minimum force F needed to push the two 75-kg cylinders up the incline. The force acts parallel to the plane and the coefficients of friction at the contacting surfaces are  A = 0.3,
A = 0.3,  B = 0.25,
B = 0.25,  C = 0.4. Each cylinder has a radius of 150 mm.
C = 0.4. Each cylinder has a radius of 150 mm.

The irregular area has a moment of inertia about the AA axis of 35 (106) mm4. If the total area is 12.0(103) mm2, determine the moment of inertia if the area about the BB axis. The DD axis passes through the centroid C of the area.
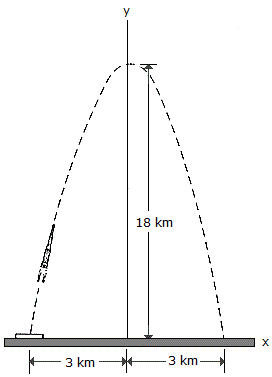
For a short time the missile moves along the parabolic path y = (18 - 2x2) km. If motion along the ground is measured as x = (4t - 3) km, where t is in seconds, determine the magnitudes of the missile's velocity and acceleration when t = 1 s.
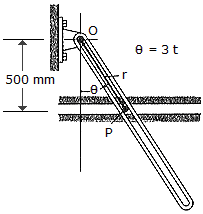
The slotted link is pinned at O, and as a result of rotation it drives the peg P along the horizontal guide. Compute the magnitude of the velocity and acceleration of P along the horizontal guide. Compute the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of P as a function of  if
if  = (3t) rad, where t is measured in seconds.
= (3t) rad, where t is measured in seconds.
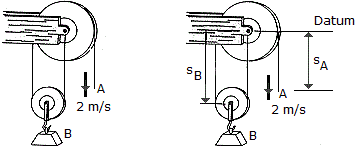
If the end of the cable at A is pulled down with a speed of 2 m/s, determine the speed at which block B arises.
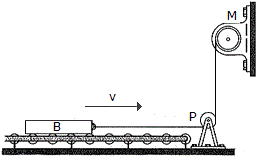
The 300-kg bar B, originally at rest, is being towed over a series of small rollers. Computer the force in the cable when t = 5s, if the motor M is drawing in the cable for a short time at a rate of v = (0.4t2) m/s, where t is in seconds (0  t
t  6 s). How far does the bar move in 5 s? Neglect the mass of the cable, pulley P, and the rollers.
6 s). How far does the bar move in 5 s? Neglect the mass of the cable, pulley P, and the rollers.
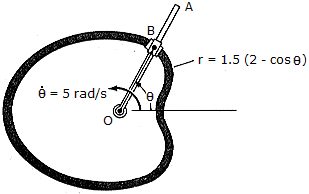
Rod OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular rate of 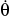 = 5 rad/s. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other slides over the horizontal curved rod, of which the shape is a limacon described by the equation r - 1.5(2 - cos
= 5 rad/s. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other slides over the horizontal curved rod, of which the shape is a limacon described by the equation r - 1.5(2 - cos  ) ft. If both collars weigh 0.75 lb, determine the normal force which the curved path exerts on one of the collars, and the force that OA exerts on the other collar at the instant
) ft. If both collars weigh 0.75 lb, determine the normal force which the curved path exerts on one of the collars, and the force that OA exerts on the other collar at the instant  = 90°.
= 90°.
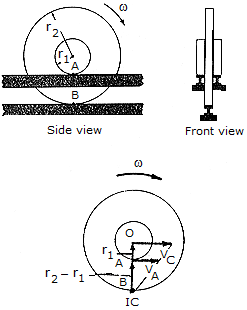
If the rim of the wheel and its hub maintain contact with the three stationary tracks as the wheel rolls, it is neccessary that slipping occurs at the hub A if no slipping occurs at B. Under these conditions, what is the speed at A if the wheel has an angular velocity  ?
?
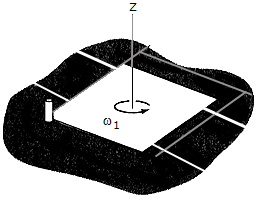
The square plate, where a = 0.75 ft, has a weight of 4 lb and is rotating on the smooth surface with a constant angular velocity of  1 = 10 rad/s. Determine the new angular velocity of the plate just after its corner strikes the peg P and the plate to rotate about P without rebounding.
1 = 10 rad/s. Determine the new angular velocity of the plate just after its corner strikes the peg P and the plate to rotate about P without rebounding.
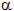 = 48.2°,
= 48.2°, 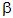 = 70.5°,
= 70.5°, 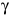 = 48.2°
= 48.2°