Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test 3
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
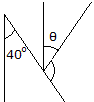
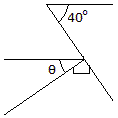
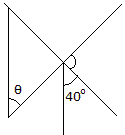
Determine the angle
 :
: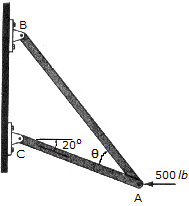
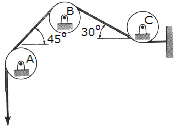
Determine the design angle  (
( <90°) bretween the two struts so that the 500-lb horizontal force has a component of 600lb directed from A toward C. That is the component of force acting along member AB?
<90°) bretween the two struts so that the 500-lb horizontal force has a component of 600lb directed from A toward C. That is the component of force acting along member AB?
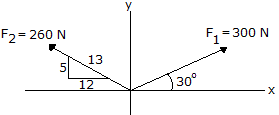
Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.

The cord is attached between two walls. If it is 8 m long, determine the distance x to the point of attachment at B.

The cable AO exerts a force on the top of the pole of F = {—120i — 90j — 80k} lb. If the cable has a length of 34 ft, determine the height z of the pole and the location (x,y) of its base.

What is the projection of the force F2 along the positive axis?

Replace the force at A by an equivalent force and couple moment at P.
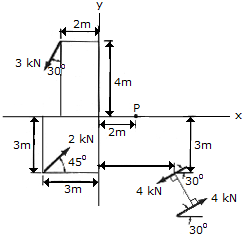
Replace the force and couple system by an equivalent single force and couple acting at point P.
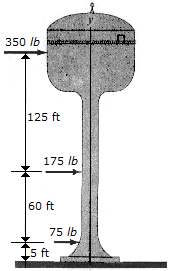
The three forces acting on the water tank represent the effect of the wind. Replace this system by a single resultant force and specify its vertical location from point O.
Compute the horizontal and vertical components of force at pin B. The belt is subjected to a tension of T=100 N and passes over each of the three pulleys.
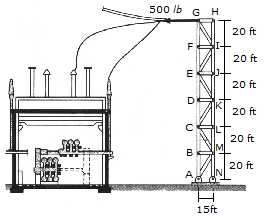
A tower used in an electrical substation supports a power line which exerts a horizontal tension of T = 500 lb on each side truss of the tower as shown. Determine the force in members BC, CM, and LM of a side truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression.
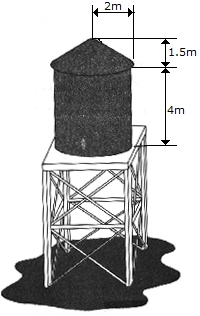
Determine the approximate amount of paint needed to cover the surface of the water storage tank. Assume that a liter of paint covers 2.5 m2. Also, what is the total inside volume of the tank.
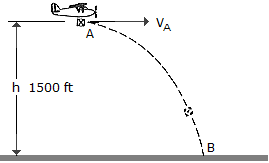
A package is dropped from the plane which is flying with a constant horizontal velocity of vA = 150 ft/s at a height h = 1500 ft. Determine the radius of curvature of the path of the package just after it is released from plane at A.
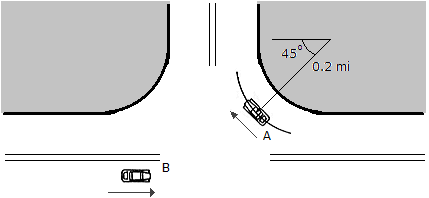
As the instant shown, cars A and B are traveling at speeds of 20 mi/h and 45 mi/h, respectively. If B is acceleration at 1600 mi/h2 while A maintains a constant speed, determine the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of A with respect to B.
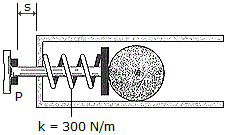
The firing mechanism of a pinball machine consists of a plunger P having a mass of 0.25 kg and a spring of stiffness k = 300 N/m. When s = 0, the spring is compressed 50 mm. If the arm is pulled back such that s = 100 mm and released, determine the speed of the 0.3 kg pinball B just before the plunger strikes the stop, i.e., s = 0. Assume all sufaces of contact to be smooth. The ball moves in the horizontal plane. Note that the ball slides without rolling.
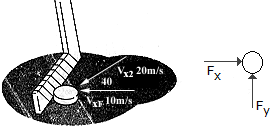
A hockey puck is traveling to the left with a velocity of v1 = 10 m/s when it is struck by a hockey stick and given a velocity of v2 = 20 m/s as shown. Determine the magnitude of the net impulse exerted by the hockey stick on the puck. The puck has a mass of 0.2 kg.
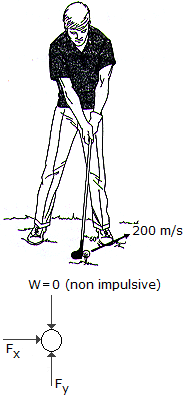
A golf ball having a mass of 40 g is struck such that it has an initial velocity of 200 m/s as shown. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the impulse given to the ball.

The motor M pulls on the cables with a force F that has a magnitude which varies as shown on the graph. If the 15-kg crate is originally resting on the floor such that the cable tension is zero when the motor is turned on, determine the speed of the crate when t = 6s.
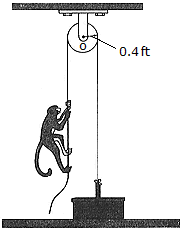
A basket and its contents weigh 10 lb. A 20-lb monkey grabs the other end of the rope and very quickly (almost instantaneously) accelerates by pulling hard on the rope until he is moving with a constant speed of vm/r = 2 ft/s measured relative to the rope. The monkey then continues climbing at this constant rate relative to the rope for 3 seconds. How fast is the basket rising at the end of the 3 seconds? Neglect the mass of the pulley and the rope.
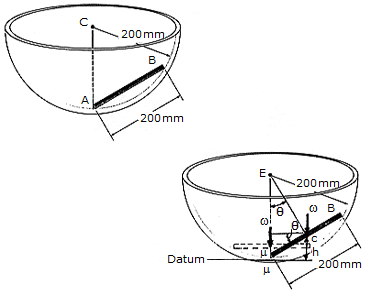
THe 500-g rod AB rests along the smooth inner surface of a hemispherical bowl. If the rod is released from the position shown, determine its angular velocity  at the instant it swings downward and becomes horizontal.
at the instant it swings downward and becomes horizontal.
 , Mp = 67.1 kN-m
, Mp = 67.1 kN-m  , Mp = 67.1 kN-m
, Mp = 67.1 kN-m 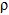 2 = 9860 ft
2 = 9860 ft