Electronics and Communication Engineering - Digital Electronics
Exercise : Digital Electronics - Section 1
- Digital Electronics - Section 13
- Digital Electronics - Section 24
- Digital Electronics - Section 23
- Digital Electronics - Section 22
- Digital Electronics - Section 21
- Digital Electronics - Section 20
- Digital Electronics - Section 19
- Digital Electronics - Section 18
- Digital Electronics - Section 17
- Digital Electronics - Section 16
- Digital Electronics - Section 15
- Digital Electronics - Section 14
- Digital Electronics - Section 1
- Digital Electronics - Section 12
- Digital Electronics - Section 11
- Digital Electronics - Section 10
- Digital Electronics - Section 9
- Digital Electronics - Section 8
- Digital Electronics - Section 7
- Digital Electronics - Section 6
- Digital Electronics - Section 5
- Digital Electronics - Section 4
- Digital Electronics - Section 3
- Digital Electronics - Section 2
36.
7BF16 = __________ 2
Answer: Option
Explanation:
7BF16 = 7 x 162 + 11 x 161 + 15 x 160 = 1983 in decimal = 0111 1011 1111 in binary.
37.
For the minterm designation Y = ∑ m (1, 3, 5, 7) the complete expression is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Decimal number 1 = binary number 001 = A BC Decimal number 7 = binary number 111= ABC, Decimal number 3 = binary number 011= ABC Decimal number 5 = binary number 101= ABC . Hence result.
38.
Zero suppression is not used in actual practice.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Zero suppression is commonly used.
39.
A counter type A/D converter contains a 4 bit binary ladder and a counter driven by a 2 MHz clock. Then conversion time
Answer: Option
Explanation:
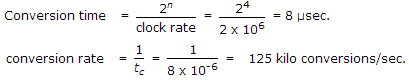
40.
The hexadecimal number (3E8)16 is equal to decimal number
Answer: Option
Explanation:
3 x 162 + 14 x 161 + 8 = 1000.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers