Electronics and Communication Engineering - Exam Questions Papers
Exercise : Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 21
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 12
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 22
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 21
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 20
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 19
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 18
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 17
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 16
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 15
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 14
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 13
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 1
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 11
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 10
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 9
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 8
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 7
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 6
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 5
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 4
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 3
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 2
1.
In a communication system, a process in which statistical averages and time averages are equal is called as,
2.
The materials not having negative temperature coefficient of resistivity are
3.
The input to a binary communication system, denoted by a random variable x, takes on one of the two values 0 or 1 with probabilities  and
and 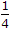 . The behaviour of the communication system is modelled by
. The behaviour of the communication system is modelled by
P(Y = 1 |x = 1|) = and P(Y = 0|x = 0) =
and P(Y = 0|x = 0) = 
Find P(Y = 1)
 and
and 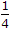 . The behaviour of the communication system is modelled by
. The behaviour of the communication system is modelled byP(Y = 1 |x = 1|) =
 and P(Y = 0|x = 0) =
and P(Y = 0|x = 0) = 
Find P(Y = 1)
4.
Consider an AM system using a square law detector as shown in figure.

XC(t) = AC[1 + u x (t)] cos ωct, |ux(t)| << 1
The signal power at the output is :

XC(t) = AC[1 + u x (t)] cos ωct, |ux(t)| << 1
The signal power at the output is :
5.
Thermal noise is passed through an ideal low-pass filter having cut-off at fc = ωHz. The auto correlation value of the noise at the output of the filter is given as
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers




