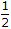Electronics and Communication Engineering - Exam Questions Papers
Exercise : Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 16
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 12
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 22
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 21
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 20
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 19
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 18
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 17
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 16
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 15
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 14
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 13
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 1
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 11
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 10
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 9
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 8
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 7
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 6
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 5
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 4
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 3
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 2
21.
Assertion (A): The small signal analysis of a transistor amplifier is done to obtain the current gain, voltage gain and the conversion efficiency of an amplifier.
Reason (R): The small signal analysis of a transistor amplifier uses the small signal parameters of the transistor.
22.
Following information is given:
- x(z) has two poles at z =
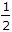 and z = - 1
and z = - 1 - x(1) = 1, x(- 1) = 1
- ROC includes
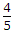
23.
Average power for  δ(t)dt signal is __________ .
δ(t)dt signal is __________ .
 δ(t)dt signal is __________ .
δ(t)dt signal is __________ .24.
The feedback configuration and the pole-zero locations of G(s)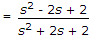 are shown below. The root locus for negative values k, i.e., for -∞ < k < 0, has breakaway/break in points and angle of departure at pole P (with respect to the positive real axis) equal to
are shown below. The root locus for negative values k, i.e., for -∞ < k < 0, has breakaway/break in points and angle of departure at pole P (with respect to the positive real axis) equal to
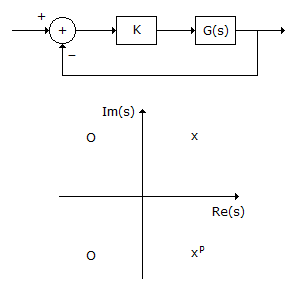
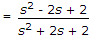 are shown below. The root locus for negative values k, i.e., for -∞ < k < 0, has breakaway/break in points and angle of departure at pole P (with respect to the positive real axis) equal to
are shown below. The root locus for negative values k, i.e., for -∞ < k < 0, has breakaway/break in points and angle of departure at pole P (with respect to the positive real axis) equal to
25.
Consider the following, logic diagram :
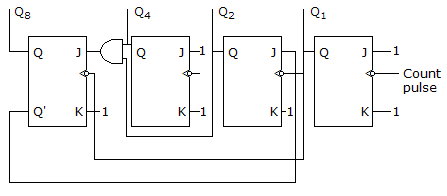
The count sequence of the above logic diagram is :

The count sequence of the above logic diagram is :
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers
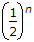 u(n) + (-1)n u(- n - 1)
u(n) + (-1)n u(- n - 1)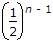 u(n - 1) + (-1)n - 1 u(- n)
u(n - 1) + (-1)n - 1 u(- n)