Electronics and Communication Engineering - Exam Questions Papers
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 12
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 22
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 21
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 20
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 19
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 18
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 17
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 16
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 15
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 14
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 13
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 1
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 11
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 10
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 9
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 8
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 7
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 6
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 5
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 4
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 3
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 2
 x + 20 cos (2 p x 108t - pz)
x + 20 cos (2 p x 108t - pz)  y. The polarization of wave is
y. The polarization of wave isThe given two components are equal in amplitude, perpendicular and out of phase by 90°.
∴ The wave is circularly polarized.
Now we consider z = 0 and put t = 0 and 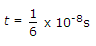
∴ At t = 0, E = 10ay
At t 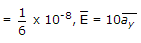
∴ Left circularly polarized.
(i) S1 - Open, S2 - Closed A1 = 0A, V1 = 4.5 V, V2 = 1.5 V, A2 = 1 A
(ii) S1 - Closed, S2 - Open A1 = 4A, V1 = 6 V, V2 = 6 V, A2 = 0 A
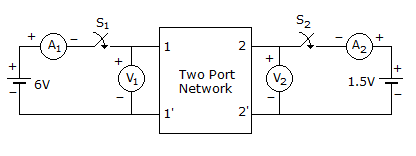
The z-parameter matrix for this network is
V1 = Z11I1 + Z12I2
V2 = Z22I + Z22I2
Using the given information; S1-open, S2-closed
4.5 = Z121 ⇒Z12 = 4.5
1.5 = Z221 ⇒ Z22 = 1.5
S1-closed, S2-open
6 = Z111 ⇒ Z11 = 1.5
6 = Z214 ⇒ Z21 = 1.5
Thus Z matrix = 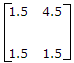
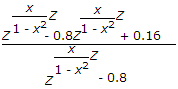 where
where 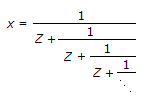
This system after practical implementation will be
Let x = 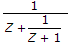
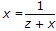
zx + x2 = 1
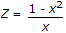
Substitute in the equation given, we get
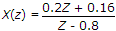
Hence we have pole at Z = 0.8 for stability the ROC should be away from Z = 0.8 towards infinity.
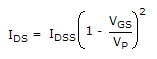
6.4 x 10-3 = 10 x 10-3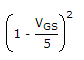
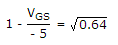 = 0.8
= 0.8
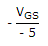 = 0.8 - 1 = - 0.2
= 0.8 - 1 = - 0.2
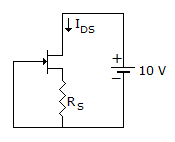
VGS = -5 x 0.2 = -1 V
IDSRS = -VGS = - (-1) = 1
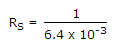 = 0.156 x 103 = 156 Ω.
= 0.156 x 103 = 156 Ω.
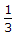 resistor.
resistor.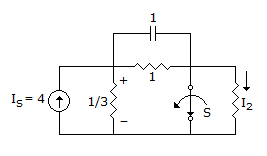
Steady state with s closed.
C is open Is = 4.
This source current is divided between two resistors 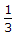 Ω and 1 Ω.
Ω and 1 Ω.
Across 1 Ω, C is open, I in 1 Ω is 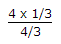 = 1 A.
= 1 A.
Hence voltage across C is 1 V. The initial charge on C is V0 = 1 V.
At t = 0+, s is opened bringing R = 1 Ω into the circuit.
C is replaced by 1 V source with positive polarity left.
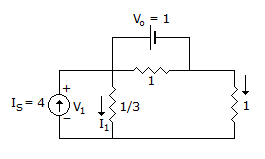
The circuit has two sources Is = 4 and V0 = 1.
The currents in the resistor R = 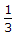 and R = 1 can be determined by superposition.
and R = 1 can be determined by superposition.
For R = 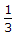
Due to Is only (short V0)
I = Is x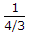 = 3
= 3
Due to V0 only (open Is)
I =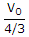 =
=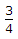 Downwards
Downwards
Adding, current through R = 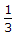 is 3
is 3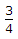 =
= 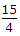 .
.
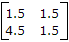
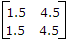
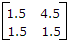
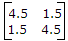
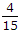 A
A