Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test 5
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.

Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
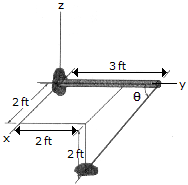
Determine the angle  between the pole AC and the wire AB.
between the pole AC and the wire AB.
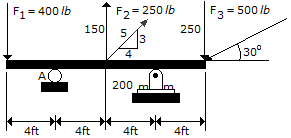
Determine the moment of force F1 about point A on the beam.

Determine the moment of the force at A about point P. Use a vector analysis and express the result in Cartesian vector form.
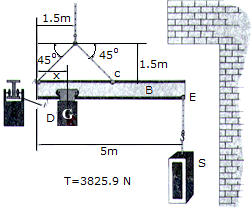
The flying boom B is used with a crane to position construction materials in coves and underhangs. The horizontal "balance" of the boom is controlled by a 250-kg block D, which has a center of gravity at G and moves by internal sensing devices along the bottom flange F of the beam. Determine the position x of the block when the boom is used to lift the stone S, which has a mass of 60 kg. The boom is uniform and has a mass of 80 kg.

Determine the tension in the supporting cables BC and BD and the components of reaction at the ball-and-socket joint A of the boom. The boom supports a drum having a weight of 200 lb. at F. Points C and D lie in the x—y plane.
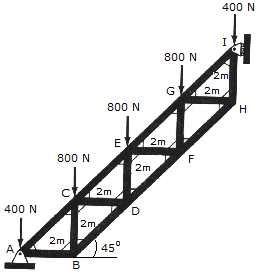
The Warren truss is used to support a staircase. Determine the force in members CE, ED, and DF, and state whether the members are in tension or compression. Assume all joints are pinned.
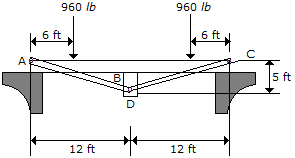
The floor beams AB and BC are stiffened using the two tie rods CD and AD. Determine the force along each rod. Assume the three contacting members at B are smooth and the joints at A, C, and D are pins.
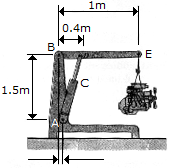
The jack shown supports a 350-kg automobile engine. Determine the compression in the hydraulic cylinder C and the magnitude of force that pin B exerts on the horizontal member BDE.
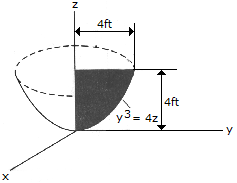
Locate the center of gravity of the volume generated by revolving the shaded area about the z axis. The material is homogeneous.
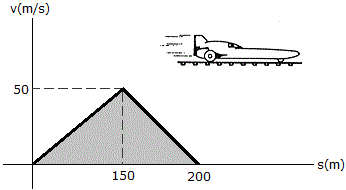
The v-s graph for a rocket sled is shown. Determine the acceleration of the sled when s = 100 m and s = 175 m.
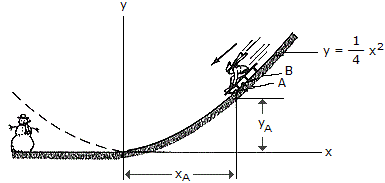
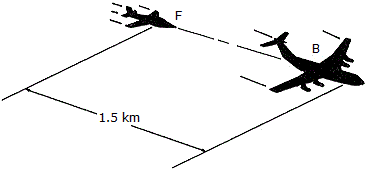
A sled is traveling down along a curve which can be approximated by the parabola y = 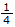 x2. When point B on the runner is coincident with point A on the curve (xA = 2m, yA = 1 m), the speed if B is measured as vB = 8 m/s and the increase in speed is dvB/dt = 4 m/s2. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.
x2. When point B on the runner is coincident with point A on the curve (xA = 2m, yA = 1 m), the speed if B is measured as vB = 8 m/s and the increase in speed is dvB/dt = 4 m/s2. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.
When the motorcyclist is at A he increases his speed along the vertical circular parth at the rate of v = (0.3t)ft/s2, where t is in seconds. If he starts from rest when he is at A, determine his velocity and acceleration when he reaches B.
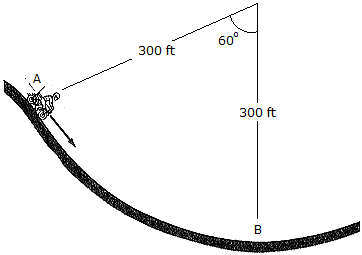
The pilot of flighter plane F is following 1.5 km behind the pilot of bomber B. Both planes are originally traveling at 120 m/s. In an effort to pass the bomber, the pilot in F gives his plane a constant acceleration of 12 m/s2. Determine the speed at which the pilot in the bomber sees the pilot of the fighter plane pass at the start of the passing operation the bomber is decelerating at 3 m/s2. Neglect the effect of any turning.
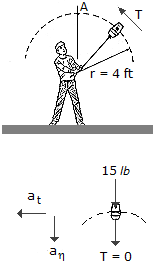
A boy twirls a 15-lb bucket of water in a vertical circle. If the radius of curvature of the path is 4 ft, determine the minimum speed the bucket must have when it is overhead at A so no water spills out.
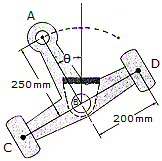
Arm ABCD is printed at B and undergoes reciprocating motion such that  = (0.3 sin 4t) rad, where t is measured in seconds and the argument for the sine is in radiaus. Determine the largest speed of point A during the motion and the magnitude of the acceleration of point D at this instant.
= (0.3 sin 4t) rad, where t is measured in seconds and the argument for the sine is in radiaus. Determine the largest speed of point A during the motion and the magnitude of the acceleration of point D at this instant.
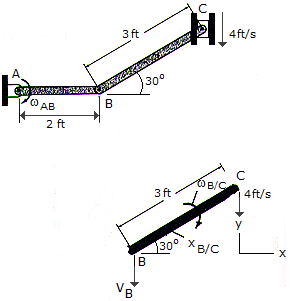
If the block at C is moving downward at 4 ft/s, determine the angular velocity of bar AB at the instant shown.
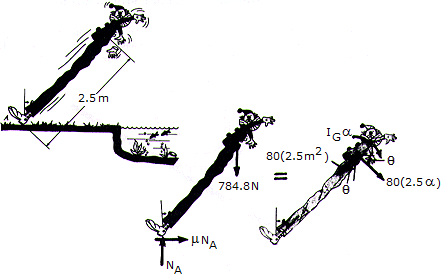
A clown, mounted on stilts, loses his balance and falls backward from the position, where it is assumed the  = 0 when
= 0 when  = 07deg;. Paralyzed with fear, he remains rigid as he falls. His mass including the stilts is 80 kg, the mass center is at G, and the radius of gyration about G is kG = 1.2 m. Determine the coefficient of friction between his shoes and the ground at A if it is observed that slipping occurs when
= 07deg;. Paralyzed with fear, he remains rigid as he falls. His mass including the stilts is 80 kg, the mass center is at G, and the radius of gyration about G is kG = 1.2 m. Determine the coefficient of friction between his shoes and the ground at A if it is observed that slipping occurs when  = 30°.
= 30°.

The slender 200-kg beam is suspended by a cable at its end as shown. If a man pushes on its other end with a horizontal force of 30 N, determine the initial acceleration of its mass center G, the beam's angular acceleration, and the tension in the cable AB.


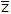 = 2.80 ft
= 2.80 ft = 0.833
= 0.833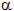 = 0.225 rad/s2, T = 1.962 kN
= 0.225 rad/s2, T = 1.962 kN