Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
16.
In a purely capacitive circuit, the current __________ the voltage by __________ .
Answer: Option
Explanation:
In inductive circuit current leads the voltage by 90°.
17.
A circuit has two branches in parallel and each branch has only one element. The applied voltage and source current are v = 200 sin (200t + 30°) and i = 50 sin (200t + 50°). If one branch has capacitor, the other branch contains
Answer: Option
Explanation:
The current is leading the voltage. Therefore, it is an RC circuit.
18.
In the circuit shown in figure, Is = 4A, Vs = 4, the voltage V is given by
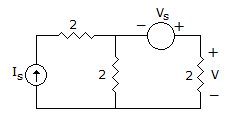

Answer: Option
Explanation:
Using superposition theorem, when Is = 0, v1 = 2 volt, when Vs = 0, current is 2A in 2Ω,
so voltage  2 x 2 = 4 volt.
2 x 2 = 4 volt.
 Net
Net  2 + 4 = 6 volt.
2 + 4 = 6 volt.
19.
The average value of wave in figure is


Answer: Option
Explanation:
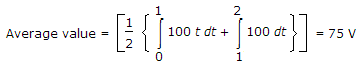
20.
If B = 4 + j3, (B)1/3 =
Answer: Option
Explanation:
4 + j3 = 5∠36.87°

Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers