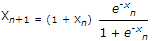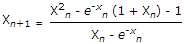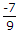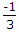Electronics and Communication Engineering - Exam Questions Papers
Exercise : Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 7
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 12
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 22
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 21
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 20
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 19
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 18
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 17
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 16
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 15
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 14
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 13
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 1
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 11
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 10
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 9
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 8
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 7
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 6
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 5
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 4
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 3
- Exam Questions Papers - Exam Paper 2
21.
A Hartley oscillator uses FET with gm of 2 ms and rd = 2 KΩ. The total coil inductance is 10 μH with turns ratio of input to output side of 1 : 10. It is tuned with a 50 pf capacitor. Find frequency of oscillations, amplifier gain margin in dB.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
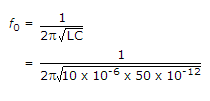
= 7.11 MHz
μ = gm x rd
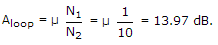
22.
The recursion relation to solve x = e-x using Newton Raphson method is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
f(xn) = xne-xn
f(xn) = 1 + e-xn f'(xn) = 1 + e-xn
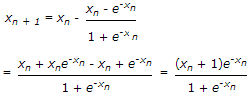
23.
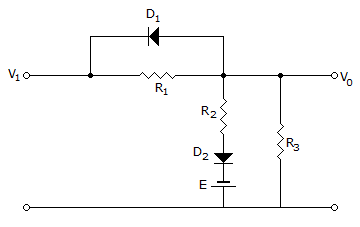
In the circuit shown in the given figure the diode states at the extremely large negative values of the input voltage vi are :

Answer: Option
Explanation:
Input V1 is extremely large negative value, so D1 is ON.
Diode D2 is shunted by R3 and the junction of R2R3 is more negative than the lower end.
Diode D2's cathode is at negative potential.
But the anode of D2 is less negative than E as the input voltage is extremely negative and D2 is OFF.
24.
Consider a baseband binary PAM receiver shown below. The additive channel noise n(t) is whit with power spectral density SN(f) = N0/2 = 10-20 W/Hz. The low-pass filter is ideal with unity gain and cutoff frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
Yk = nNk if transmitted bit bk = 0
Yk = a + Nk if transmitted bit bk = 1
Where Nk represents the noise sample value. The noise sample has a probability density function, PNk(n) = 0.5ae-a|n| (This has mean zero and variance 2/a2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2 = 10-6 V.

The value of the parameter a (in V-1) is
Yk = nNk if transmitted bit bk = 0
Yk = a + Nk if transmitted bit bk = 1
Where Nk represents the noise sample value. The noise sample has a probability density function, PNk(n) = 0.5ae-a|n| (This has mean zero and variance 2/a2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2 = 10-6 V.

The value of the parameter a (in V-1) is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
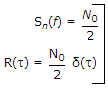
→ exist in fourier transform
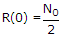
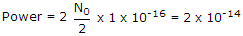
Variance = 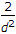 which is equal to power since mean is zero ⇒ a = 107.
which is equal to power since mean is zero ⇒ a = 107.
25.
The probability density function of a random variable x is as shown.
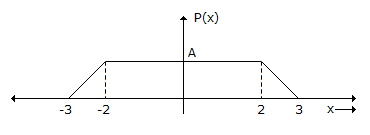
The mean of the distribution is:

The mean of the distribution is:
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Mean of the distribution = 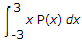
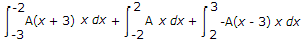
A = 1/5 then find mean.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers