Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4 (Q.No. 24)
24.
In given figure a silicon diode is carrying a constant current of 1 mA. When the temperature of the diode is 20°C, VD is found to be 700 mV. If the temperature rises to 40°C, VD becomes approximately equal to
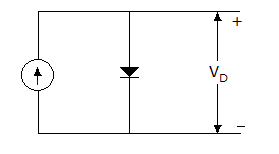

Answer: Option
Explanation:
Id = Io(eVD/ηVT - 1)
By considering 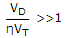 , then
, then

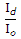 = eVD/ηVT
= eVD/ηVT

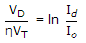
Id is constant according to question,
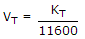
 VD a T
VD a T

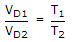

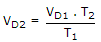
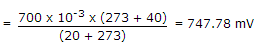 .
.
Discussion:
3 comments Page 1 of 1.
Saurabh kumar said:
5 years ago
Option B is the right option
when junction temperature increases current also increases and voltage decreases
every 10-degree rise temperature of 20 mv decreases junction voltage.
So new juntion voltage is about (700 - 20 * 2) = 660mv.
when junction temperature increases current also increases and voltage decreases
every 10-degree rise temperature of 20 mv decreases junction voltage.
So new juntion voltage is about (700 - 20 * 2) = 660mv.
Charmin said:
9 years ago
Yes this is wrong.
As 1 degree 2.5mv drop so 40-20 = 20 * 2.5 = 50 then 700-50 = 650~660.
As 1 degree 2.5mv drop so 40-20 = 20 * 2.5 = 50 then 700-50 = 650~660.
Kshama said:
10 years ago
For every 1 degree Celsius, the rise in the temperature and the voltage decreases by 2.3mv per degree Celsius.
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers