Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.

Express each force in Cartesian vector form.

Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.

The cable AO exerts a force on the top of the pole of F = {—120i — 90j — 80k} lb. If the cable has a length of 34 ft, determine the height z of the pole and the location (x,y) of its base.
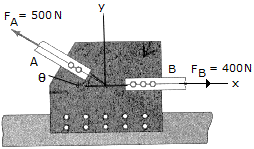
Determine the design angle  for connecting member A to the plate if the resultant force is to be directed vercially upward. Also, what is the magnitude of the resultant?
for connecting member A to the plate if the resultant force is to be directed vercially upward. Also, what is the magnitude of the resultant?
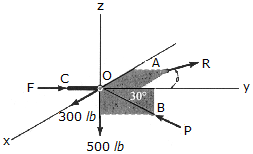
The joint O of a space frame is subjected to four forces. Strut OA lies in the x-y plane and strut OB lies in the y-z plane. Determine the force acting in each if the three struts required for equilibrium of the joint. Set  = 45°.
= 45°.
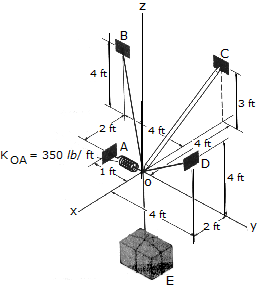
Determine the tension developed in cables OD and OB and the strut OC, required to support the 500-lb crate. The spring OA has an unstretched length of 0.2 ft and a stiffness of kOA = 350lb/ft. The force in the strut acts along the axis of the strut.
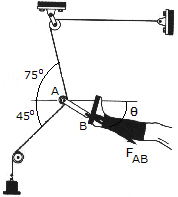
Determine the magnitude and direction  of the resultant force FAB exerted along link AB by the tractive apparatus shown. The suspended mass is 10 kg. Neglect the size of the pulley at A.
of the resultant force FAB exerted along link AB by the tractive apparatus shown. The suspended mass is 10 kg. Neglect the size of the pulley at A.
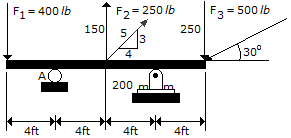
Determine the moment of force F1 about point A on the beam.

Replace the force at A by an equivalent force and couple moment at P.

Determine the radius of gyration ky of the parabolic area.
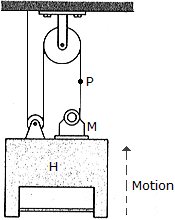
If the hoist H is moving upward at 6 ft/s, determine the speed at which the motor M must draw in the supporting cable.
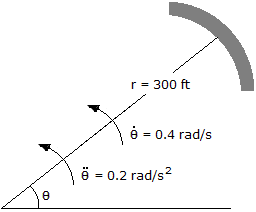
A car is traveling along the circular curve of radius r = 300 ft. At the instant shown, its angular rate of rotation is  = 0.4 rad / s, which is increasing at the rate of
= 0.4 rad / s, which is increasing at the rate of 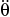 = 0.2 rad / s2. Determine the magnitude of the velocity of the car at this instant.
= 0.2 rad / s2. Determine the magnitude of the velocity of the car at this instant.

A 1.5-lb brick is released from rest A and slides down the inclined roof. If the coefficient of friction between the roof and the brick is  = 0.3, determine the speed at which the brick strikes the gutter G.
= 0.3, determine the speed at which the brick strikes the gutter G.
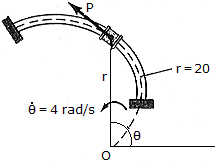
The spool, which has a weight of 2lb, slides along the smooth horizontal spiral rod, r = (2 ) ft, where
) ft, where  is in radians. If its angular rate of rotation is constant and equals
is in radians. If its angular rate of rotation is constant and equals 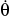 = 4 rad/s, determine the tangential force P needed to cause the motion and the normal force that the spool exerts on the rod at the instant
= 4 rad/s, determine the tangential force P needed to cause the motion and the normal force that the spool exerts on the rod at the instant  = 90°.
= 90°.
A stunt driver in car A travels in free flight off the edge of a ramp at C. At the point of maximum height he strikes car B. If the direct collision is perfectly plastic (e = 0), determine the required ramp speed vC at the end of the ramp C, and the approximate distance s where both cars strike the ground. Each car has a mass of 3.5 Mg. Neglect the size of the cars in the calculation.
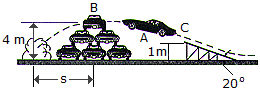
A golf ball having a mass of 40 g is struck such that it has an initial velocity of 200 m/s as shown. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the impulse given to the ball.
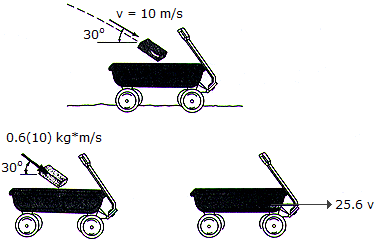
A 0.6-kg brick is thrown into a 25-kg wagon which is initially at rest. If, upon entering, the brick has a velocity of 10 m/s as shown, determine the final velocity of the wagon.
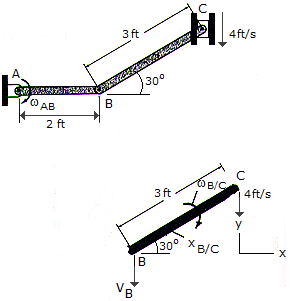
If the block at C is moving downward at 4 ft/s, determine the angular velocity of bar AB at the instant shown.

A cord wrapped around the inner core of a spool. If the cord is pulled with a constant tension of 30 lb and the spool is originally at rest, determine the spool's angular Velocity when s = 8 ft of cord have unraveled. Neglect the weight of the cord. The spool and cord have a total weight of 400 lb and the radius of gyration about the axle A is kA = 1.30 ft.
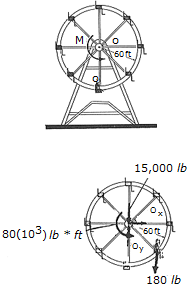
A man having a weight of 180 lb sits in a chair of the Ferris wheel, which has a weight of 15,000 lb and a radius of gyration of ko = 37 ft. If a torque of M = 80(103) lb • ft is applied about O, determine the angular velocity of the wheel after it has rotated 180°. Neglect the weight of the chairs and note that the man remains in an upright position as the wheel rotates. The wheel starts from rest in the position shown.


 = 6.73 rad/s
= 6.73 rad/s