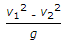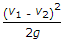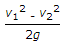Mechanical Engineering - Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Section 1 (Q.No. 11)
11.
The length AB of a pipe ABC in which the liquid is flowing has diameter (d1) and is suddenly enlarged to diameter (d2) at B which is constant for the length BC. The loss of head due to sudden enlargement is
Discussion:
32 comments Page 2 of 4.
Rohit singh said:
8 years ago
I think option D is the correct option.
Andrew Han said:
8 years ago
Why not D?
PRABHA said:
9 years ago
Answer C is Correct one.
Srinivas said:
9 years ago
Z1 is not equal to z2 in this case.
So the answer is 'c'.
So the answer is 'c'.
Anant said:
9 years ago
Option C is correct. I agree with the given answer.
Niranjan Bisht said:
9 years ago
Opt-c is correct as sudden enlargement of pipe, so change in momentum is also taken into acc.
Amresh kumar sinha said:
1 decade ago
Bernaullie's principle: As with having different areas of flow of a fluid through a convergent pipe,give us a reason to apply conservation of energy equation having relation with pressure,velocity and density of the respective fluid.
As for a pipe having two ends with different dimensions of respectively pressure,velocity and densities then we have the equation as-{(p1/wg+v1square/2g+z1)-(p2/wg+v2square/2g+z2)}=constant.
As for a pipe having two ends with different dimensions of respectively pressure,velocity and densities then we have the equation as-{(p1/wg+v1square/2g+z1)-(p2/wg+v2square/2g+z2)}=constant.
Anandan said:
9 years ago
Please give the correct explanation for option D.
Yogita said:
9 years ago
The correct answer should be D.
ANKIT GUPTA said:
9 years ago
Here the answer should be D.
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers