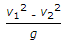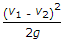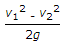Mechanical Engineering - Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Section 1 (Q.No. 11)
11.
The length AB of a pipe ABC in which the liquid is flowing has diameter (d1) and is suddenly enlarged to diameter (d2) at B which is constant for the length BC. The loss of head due to sudden enlargement is
Discussion:
32 comments Page 1 of 4.
Amresh kumar sinha said:
1 decade ago
Bernaullie's principle: As with having different areas of flow of a fluid through a convergent pipe,give us a reason to apply conservation of energy equation having relation with pressure,velocity and density of the respective fluid.
As for a pipe having two ends with different dimensions of respectively pressure,velocity and densities then we have the equation as-{(p1/wg+v1square/2g+z1)-(p2/wg+v2square/2g+z2)}=constant.
As for a pipe having two ends with different dimensions of respectively pressure,velocity and densities then we have the equation as-{(p1/wg+v1square/2g+z1)-(p2/wg+v2square/2g+z2)}=constant.
Ballamudi mounica said:
1 decade ago
We know the Bernoulli's equation.
From that we obtain,
p1/wg+v1^2/2g+z1 = p2/wg+v2^2/2g+z2.
z1=z2 from this we get,
p1/wg-p2/wg = v1^2/2g-v2^2/2g.
= (v1-v2)^2/2g.
Which is loss of head bcoz p1-p2/wg=H where h=head loss
and wg=row.
From that we obtain,
p1/wg+v1^2/2g+z1 = p2/wg+v2^2/2g+z2.
z1=z2 from this we get,
p1/wg-p2/wg = v1^2/2g-v2^2/2g.
= (v1-v2)^2/2g.
Which is loss of head bcoz p1-p2/wg=H where h=head loss
and wg=row.
Anup Kumar said:
1 decade ago
I Think that Answer is D.
Becoz according to Bernoulli's Equation.
H = P1/wg-p2/wg = (v1^2-v2^2)/2g.
Becoz according to Bernoulli's Equation.
H = P1/wg-p2/wg = (v1^2-v2^2)/2g.
MD MOBIN ALAM said:
1 decade ago
Minor losses due to sudden expansion By bernoulli's eq.
h=(v1^ 2-v2^2/2g)-(p1-p2/$g).
And by momentum eq,
(p1-p2/$g)=v2(v2-v1)/g and put the value in above eq,
Then,
h=(v1-v2)^2/2g.
h=(v1^ 2-v2^2/2g)-(p1-p2/$g).
And by momentum eq,
(p1-p2/$g)=v2(v2-v1)/g and put the value in above eq,
Then,
h=(v1-v2)^2/2g.
Leena 2016 said:
10 years ago
Option D should be the answer.
Nitesh kumar mishra said:
10 years ago
I am sure, that option "D" should be the correct answer.
Piyush Rathore said:
10 years ago
D is the correct option. I am damn sure about it.
Sthitadhi Ghosh said:
9 years ago
Option D is the correct answer.
Rvv said:
9 years ago
Yes, agree D is correct answer.
Satyam singh said:
9 years ago
Can some explain how answer C is correct?
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers