Engineering Mechanics - Structural Analysis
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Structural Analysis"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Structural Analysis" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Structural Analysis"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "Structural Analysis" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "Structural Analysis" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "Structural Analysis" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Structural Analysis" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "Structural Analysis" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "Structural Analysis"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "Structural Analysis" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- Structural Analysis - General Questions
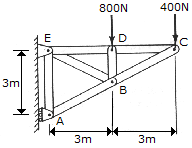
Determine the force in each member of the truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression.

The principles of a differential chain block are indicated schematically in the figure. Determine the magnitude of force P needed to support the 800-N force. Also compute the distance x where the cable must be attached to bar AB so the bar remains horizontal. All pulleys have a radius of 60 mm.
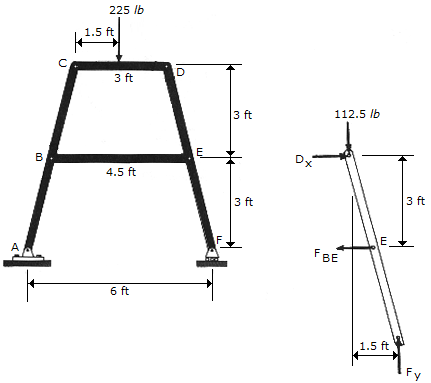
Determine the magnitude of the forces in pins B and D of the four-member frame.

Determine the force in members FF, FB, and BC of the Fink truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression.
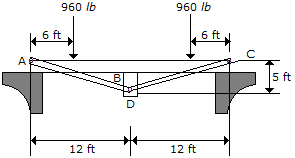
The floor beams AB and BC are stiffened using the two tie rods CD and AD. Determine the force along each rod. Assume the three contacting members at B are smooth and the joints at A, C, and D are pins.