Engineering Mechanics - PKRB: Force and Animation
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Force and Animation"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Force and Animation" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Force and Animation"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "PKRB: Force and Animation" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "PKRB: Force and Animation" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "PKRB: Force and Animation" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Force and Animation" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "PKRB: Force and Animation" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "PKRB: Force and Animation"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "PKRB: Force and Animation" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- PKRB: Force and Animation - General Questions

The slender 200-kg beam is suspended by a cable at its end as shown. If a man pushes on its other end with a horizontal force of 30 N, determine the initial acceleration of its mass center G, the beam's angular acceleration, and the tension in the cable AB.
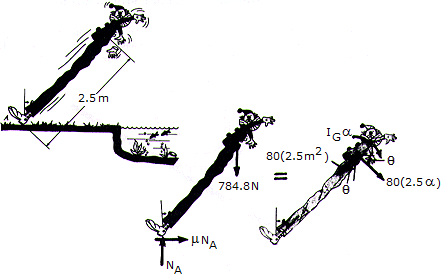
A clown, mounted on stilts, loses his balance and falls backward from the position, where it is assumed the  = 0 when
= 0 when  = 07deg;. Paralyzed with fear, he remains rigid as he falls. His mass including the stilts is 80 kg, the mass center is at G, and the radius of gyration about G is kG = 1.2 m. Determine the coefficient of friction between his shoes and the ground at A if it is observed that slipping occurs when
= 07deg;. Paralyzed with fear, he remains rigid as he falls. His mass including the stilts is 80 kg, the mass center is at G, and the radius of gyration about G is kG = 1.2 m. Determine the coefficient of friction between his shoes and the ground at A if it is observed that slipping occurs when  = 30°.
= 30°.
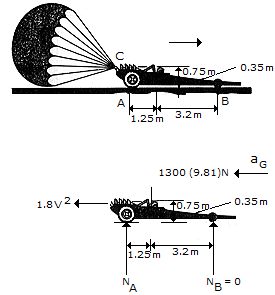
The dragster has a mass of 1.3 Mg and a center of mass at G. If a braking parachute is attached at C and provides a horizontal braking force FD, determine the maximum deceleration the dragster can have upon releasing the parachute without tipping the dragster over backwards (i.e., the normal force under the wheels and assume that the engine is disengaged so that the wheels are freely rolling.

The sports car has a mass of 1.5 Mg and a center of mass at G. Determine the shortest time it takes for it to reach a speed of 80 km/h, starting from rest, if the engine only drives the rear wheels, whereas the front wheels are free rolling. The coefficient of friction between the wheels and road is  = 0.2. Neglect the mass of the wheels for the calculation.
= 0.2. Neglect the mass of the wheels for the calculation.

The disk has a mass of 20 kg and is originally spinning at the end of the massless strut with an angular velocity of  = 60 rad/s. If it is then placed against the wall, for which
= 60 rad/s. If it is then placed against the wall, for which  A = 0.3, determine the time required for the motion to stop. What is the force in strut BC during this time?
A = 0.3, determine the time required for the motion to stop. What is the force in strut BC during this time?
 = 0.225 rad/s2, T = 1.962 kN
= 0.225 rad/s2, T = 1.962 kN