Engineering Mechanics - Force Vectors
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Force Vectors"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Force Vectors" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Force Vectors"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "Force Vectors" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "Force Vectors" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "Force Vectors" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "Force Vectors" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "Force Vectors" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "Force Vectors"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "Force Vectors" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- Force Vectors - General Questions

The cord is attached between two walls. If it is 8 m long, determine the distance x to the point of attachment at B.

Determine the magnitude of the resultant force by adding the rectangular components of the three forces.
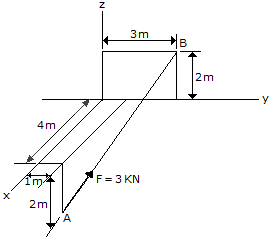
Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then determine its direction angles.

Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
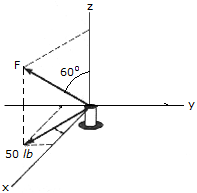
Force F acts on peg A such that one of its components, lying in the x-y plane, has a magnitude of 50 lb. Express F as a Cartesian vector.
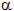 = 48.2°,
= 48.2°, 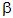 = 70.5°,
= 70.5°, 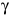 = 48.2°
= 48.2° = 106.2° CCW
= 106.2° CCW