Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
36.
The current wave of figure, is passed through a 3 H inductor during the period 0 to 2 seconds
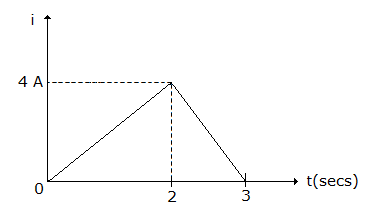

Answer: Option
Explanation:
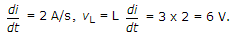
37.
The minimum number of equations required to analyze the circuit shown in the figure is
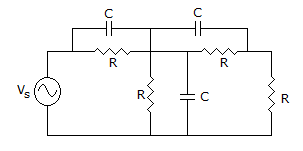

Answer: Option
Explanation:
No. of loop = No. of equations = b - n + 1  7 - 4 + 1
7 - 4 + 1  4.
4.
38.
If Z(s) has a pole at origin, the realization leads to
Answer: Option
Explanation:
In such a function the denominator is one degree higher than the numerator.
Therefore we get a term 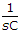 . Hence, the network has capacitance in series.
. Hence, the network has capacitance in series.
39.
A series resonant circuit has inductance L. If L is increased, the resonant frequency
Answer: Option
Explanation:
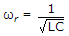 . As L increases ωr decreases.
. As L increases ωr decreases.
40.
In a coupled coil the primary has 100 turns and secondary has 200 turns. The primary produces, a flux Φ = e-t. The coefficient of coupling is 1. The voltages induced in secondary is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
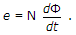
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers