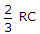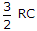Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
26.
A network has 10 nodes and 17 branches. The number of different node pair are
Answer: Option
Explanation:
One node is reference node. Therefore the system has 9 node pairs.
27.
In a series RC circuit Z = (R2 + ω2C2)0.5.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
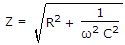
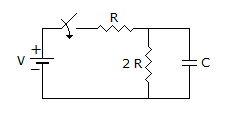
28.
The time constant of the network shown in figure is

Answer: Option
Explanation:
Time constant t = C Req
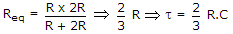 .
.
29.
If V = 20 + j20, then loge(A) A is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
20 x j 20 = 28.28 Ð45° loge V = loge (28.28) + 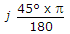 = 3.342 j.785.
= 3.342 j.785.
30.
In an ac network the sum of currents entering a node is 10 ∠45°. The sum of currents leaving the node is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
As per KCL sum of currents entering a node is equal to sum of currents leaving a node.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers