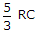Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits
Exercise : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 24
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 14
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 27
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 26
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 25
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 24
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 23
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 22
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 21
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 20
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 19
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 18
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 17
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 16
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 15
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 13
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 12
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 10
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 8
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 7
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 6
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 5
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 2
46.
The voltage of single phase supply to residential consumers in India is
47.
Power factor of the following circuit will be unity
48.
In the transformer shown in figure, the inductance measured across terminal 1 and 2 was 4 H with terminals 3 and 4 open. It was 3H when terminals 3 and 4 are short circuited. The coefficient of coupling is
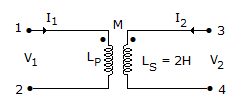
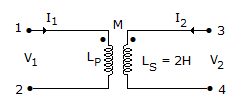
49.
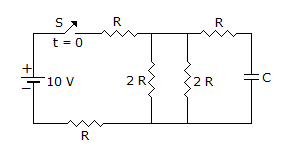
The time constant of the network shown in figure is, when switch is closed.

50.
For an ideal transformer
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers