Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits
Exercise : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 21
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 14
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 27
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 26
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 25
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 24
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 23
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 22
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 21
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 20
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 19
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 18
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 17
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 16
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 15
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 13
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 12
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 10
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 8
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 7
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 6
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 5
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 2
21.
Hysteresis loss is proportional to
22.
When a lead acid battery is fully charged the colours of its positive and negative plates are
23.
Two independence parameters Z11 and Z12 of the two-port network in the figure are
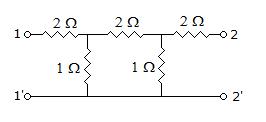
24.
Network transients are due to
25.
The Laplace transform of i(t) is given by 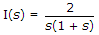 As t → ∞ the value of i(t), tends to
As t → ∞ the value of i(t), tends to
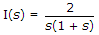 As t → ∞ the value of i(t), tends to
As t → ∞ the value of i(t), tends toQuick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers