Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits
Exercise : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 14
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 27
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 26
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 25
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 24
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 23
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 22
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 21
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 20
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 19
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 18
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 17
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 16
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 15
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 13
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 12
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 10
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 8
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 7
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 6
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 5
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 2
16.
A wave trap is a
Answer: Option
Explanation:
It has R and L in one branch and a variable capacitance in second branch.
17.
In following circuit, steady state is reached with S open, S is closed at t = 0, the current I at t = 0+ is given by
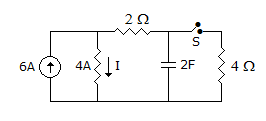

Answer: Option
Explanation:
When steady state is reached with s open, capacitor will act as open circuit
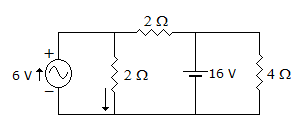
Current in 4Ω resistor will be = 6A at steady state.
Voltage across 4Ω = 6 x 4  24 volt.
24 volt.
Current in 2Ω resistor due to 6A  3A current due to 16 V, source.
3A current due to 16 V, source.
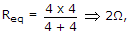 I = 16/2
I = 16/2  8A, this current divide in (2 + 2) Ω is 4Ω resistor current in 2Ω resistor
8A, this current divide in (2 + 2) Ω is 4Ω resistor current in 2Ω resistor  4A + 3A
4A + 3A  7A.
7A.
18.
In an ac series RLC circuit the maximum phase difference between any two voltages can be
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Voltage across inductance leads the current by 90° and voltage across capacitance lags the current by 90°.
19.
In a series circuit with XL constant and R variable the current locus lies in the third quadrant.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
it lies in fourth quadrant.
20.
One coulomb charge is equal to the charge on
Answer: Option
Explanation:
As per definition 1C = 6.24 x 1018 electrons.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers