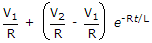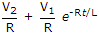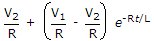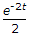Electronics and Communication Engineering - Electronic Devices and Circuits
Exercise : Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 14
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 27
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 26
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 25
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 24
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 23
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 22
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 21
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 20
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 19
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 18
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 17
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 16
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 15
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 1
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 13
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 12
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 11
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 10
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 9
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 8
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 7
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 6
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 5
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 4
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 3
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Section 2
46.
For the wave shown in figure, the average value is
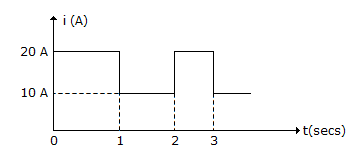
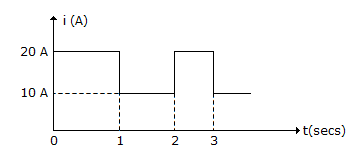
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Average value = 10 + 0.5 x 10 = 15 A.
47.
The dc voltage applied to an R-L series circuit is suddenly changed from V1 to V2. The expression for transient current is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
The final steady state current is 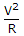 and transient term must depend on both V1 and V2.
and transient term must depend on both V1 and V2.
48.
One ampere means the flow of
Answer: Option
Explanation:
As per definition one ampere means 1 coulomb per second.
49.
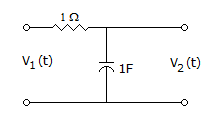
For the following circuit a source of V1(t) = e-2t is applied, then the resulting response V2(t) is given by

Answer: Option
Explanation:
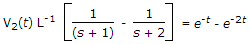 .
.
50.
When R and C are connected in parallel, phase angle of Y is positive.
Answer: Option
Explanation:
I = YV. Since I leads V, phase angle of Y must be positive.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers