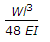Online Mechanical Engineering Test - Strength of Materials Test 1
Instruction:
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Total number of questions
20
Number of answered questions
0
Number of unanswered questions
20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
1.
The maximum diameter of the hole that can be punched from a plate of maximum shear stress 1/4th of its maximum crushing stress of punch, is equal to (where t = Thickness of the plate)
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
2.
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
3.
A body is subjected to two normal stresses 20 kN/m2 (tensile) and 10 kN/m2 (compressive) acting perpendicular to each other. The maximum shear stress is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
4.
The shear force at apoint on a beam is the algebraic __________ of all the forces on either side of the point.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
5.
When the shear force diagram is a parabolic curve between two points, it indicates that there is a
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
6.
The polar modulus for a solid shaft of diameter (D) is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
7.
The volumetric strain is the ratio of the
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
8.
The design of thin cylindrical shells is based on
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
9.
The torque transmitted by a hollow shaft of outer diameter (D) and inner diameter (d) is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
10.
The strength of a riveted joint is equal to the
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
11.
The maximum shear stress in a thin cylindrical shell subjected to internal pressure p is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
12.
The assumption, generally, made in the theory of simple bending is that
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
13.
The values of equivalent length (L) and actual length (l) of a column for both ends hinged is the same
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
14.
The centre to centre distance, between two consecutive rivets in a row, is called
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
15.
In a stress-strain diagram for mild steel, as shown in the below figure, the point A represents


Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
16.
When a load on the free end of a cantilever beam is increased, failure will occur
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
17.
A simply supported beam 'A' of length l, breadth b, and depth d carries a central point load W. Another beam 'B' has the same length and depth but its breadth is doubled. The deflection of beam 'B' will be __________ as compared to beam 'A'.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
18.
The shear modulus of most materials with respect to the modulus of elasticity is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
19.
For a beam, as shown in the below figure, the deflection at C is (where E = Young's modulus for the beam material, and I = Moment of inertia of the beam section. )


Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
20.
The critical neutral axis of a reinforced cement concrete beam is based on the principle that the neutral axis is situated at the centre of gravity of a given section.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Strength of Materials
*** END OF THE TEST ***
Time Left: 00:29:56
Post your test result / feedback here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers