Online Electronic Devices Test - Electronic Devices Test 5
Instruction:
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Total number of questions
20
Number of answered questions
0
Number of unanswered questions
20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
1.
In n-type material the ________ is called the majority carrier.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Semiconductor Diodes
2.
What best describes the circuit?
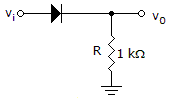
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Diode Applications
3.
The output frequency of a full-wave rectifier is ________ the input frequency.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Diode Applications
4.
In what decade was the first transistor created?
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : BJT Devices
5.
Calculate the approximate value of the maximum power rating for the transistor represented by the output characteristics of Figure 4.1?
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : DC Biasing-BJTs
6.
What is the unit of the parameter ho?
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : BJT Amplifiers
7.
Refer to the following characteristic curve. Calculate the resistance of the FET at VGS = –0.25 V if ro = 10 k .
.
 .
. 
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : FET Devices
8.
For ________, Shockley's equation is applied to relate the input and the output quantities.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : DC Biasing-FETs
9.
Which operation class is generally used in radio or communications?
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Power Amplifiers
10.
Class B operation is provided when the dc bias leaves the transistor biased just off, the transistor turning on when the ac signal is applied.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Power Amplifiers
11.
A silicon power transistor is operated with a heat sink (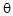 SA = 1.5ºC/W). The transistor, rated at 150 W (25ºC), has
SA = 1.5ºC/W). The transistor, rated at 150 W (25ºC), has 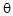 JC = 0.5º C/W, and the mounting insulation has
JC = 0.5º C/W, and the mounting insulation has 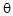 CS = 0.6 ºC/W. What is the maximum power that can be dissipated if the ambient temperature is 50ºC and TJmax = 200 ºC?
CS = 0.6 ºC/W. What is the maximum power that can be dissipated if the ambient temperature is 50ºC and TJmax = 200 ºC?
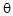 SA = 1.5ºC/W). The transistor, rated at 150 W (25ºC), has
SA = 1.5ºC/W). The transistor, rated at 150 W (25ºC), has 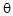 JC = 0.5º C/W, and the mounting insulation has
JC = 0.5º C/W, and the mounting insulation has 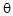 CS = 0.6 ºC/W. What is the maximum power that can be dissipated if the ambient temperature is 50ºC and TJmax = 200 ºC?
CS = 0.6 ºC/W. What is the maximum power that can be dissipated if the ambient temperature is 50ºC and TJmax = 200 ºC?Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Power Amplifiers
12.
Which of the following applications include a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit?
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Linear-Digital ICs
13.
The start-up gain of an oscillator must be ________ one.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Oscillator Circuits
14.
A type of regulator circuit that is quite popular for its efficient transfer of power to the load is the ________.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Voltage Regulators
15.
A reverse-biased silicon diode has about 0.7 V across it.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Semiconductors
16.
For a given input frequency, a half-wave rectifier is easier to filter than a full-wave rectifier.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Diode Applications
17.
VRRM is the same as PIV rating.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Diode Applications
18.
Refer to the given figure. The most probable cause of trouble, if any, from these voltage measurements is
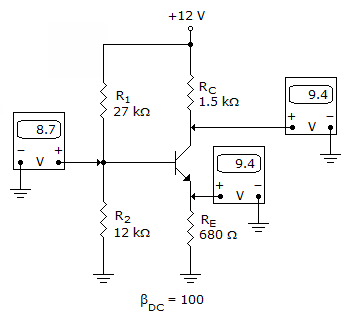

Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Transistor Bias Circuits
19.
Collector-feedback bias is another name for base bias.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Transistor Bias Circuits
20.
Refer to the given figure. ID = 6 mA. Calculate the value of VDS.
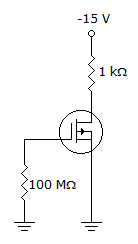
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Field-Effect Transistors
*** END OF THE TEST ***
Time Left: 00:29:56
Post your test result / feedback here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers