Non Verbal Reasoning - Cubes and Dice
- Cubes and Dice - Introduction
- Cubes and Dice - Section 1
- Cubes and Dice - Section 2
Three different positions X, Y and Z of a dice are shown in the figures given below. Which number lies at the bottom face in position X?
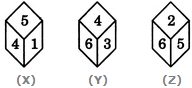
From positions X and Y we conclude that 1, 5, 6 and 3 lie adjacent to 4. Therefore, 2 must lie opposite 4. From positions Y and Z we conclude that 4, 3, 2 and 5 lie adjacent to 6. Therefore, 1 must lie opposite 6. Thus, 2 lies opposite 4, 1 lies opposite 6 and consequently 5 lies opposite 3.
As analysed above, the number on the face opposite 5 is 3. In position X, since 5 lies on the top, therefore 3 must lie at the bottom face.
A dice is numbered from 1 to 6 in different ways.
If 2 is opposite to 3 and adjacent to 4 and 6, then which of the following statements is necessarily true?
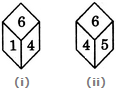
Two positions of a dice are shown below. When number 1 is on the top, what number will be at the bottom?
Two positions of a cube are shown below. When the number 4 will be at the bottom, then which number will be at the top?
Two positions of a block are shown below: When six is at the bottom, what number will be at the top?
