Non Verbal Reasoning - Cubes and Dice
- Cubes and Dice - Introduction
- Cubes and Dice - Section 1
- Cubes and Dice - Section 2
Two positions of a dice are shown below: When 2 is at the bottom, what number will be at the top?
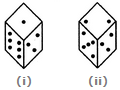
A dice is numbered from 1 to 6 in different ways.
If 1 is opposite to 5 and 2 is opposite to 3, then
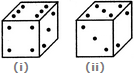
Two positions of a block are shown below. When 2 is at the bottom, which number will be at the top?
Three different positions X, Y and Z of a dice are shown in the figures given below. Which numbers are hidden behind the numbers 6 and 5 in the position Z?
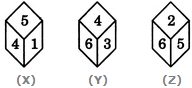
From positions X and Y we conclude that 1, 5, 6 and 3 lie adjacent to 4. Therefore, 2 must lie opposite 4. From positions Y and Z we conclude that 4, 3, 2 and 5 lie adjacent to 6. Therefore, 1 must lie opposite 6. Thus, 2 lies opposite 4, 1 lies opposite 6 and consequently 5 lies opposite 3.
As analysed above, the number opposite 6 is 1 and the number opposite 5 is 3. Therefore, the numbers hidden behind the numbers 6 and 5 in position Z (these are the numbers opposite 5 and 6 respectively) are 1 and 3.
Four positions of a dice are shown below. What number must be at the bottom face when the dice is in the position as shown in the figure(iii)

From figures (i), (ii), (iv) we conclude that 5, 6, 1 and 2 lie adjacent to 4. Hence, 3 must lie opposite 4 and vice-versa. In fig. (iii), 3 is at the top and consequently 4 must lie at the bottom face.