Engineering Mechanics - KOP: Work and Energy
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Work and Energy"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Work and Energy" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Work and Energy"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "KOP: Work and Energy" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "KOP: Work and Energy" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "KOP: Work and Energy" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Work and Energy" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "KOP: Work and Energy" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "KOP: Work and Energy"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "KOP: Work and Energy" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- KOP: Work and Energy - General Questions

The elevator E and its freight have a total mass of 400 kg. Hoisting is provided by the motor M and the 60-kg block C. If the motor has an efficiency of e = 0.6, determine the power that must be supplied to the motor when the elevator is hoisted upward at a constant speed of vE = m/s.
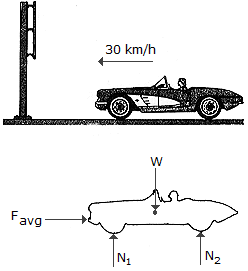
A car having a mass of 2 Mg strikes a smooth, rigid sign post with an initial speed of 30 km/h. To stop the car, the front end horizontally deforms 0.2 m. If the car is free to roll during the collision, determine the average horizontal collision force causing the deformation.
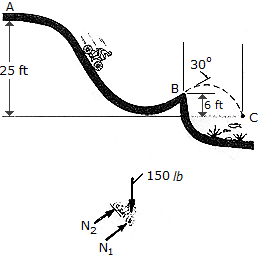
When at A the bicyclist has a speed of vA = ft/s. If he coasts without pedaling from the top of the hill at A to the shore of B and then leaps off the shore, determine his speed at B and the distance x where he strikes the water at C. The rider and his bicycle have a total weight of 150 lb. Neglect the size of the bicycle and wind resistance.
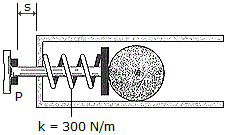
The firing mechanism of a pinball machine consists of a plunger P having a mass of 0.25 kg and a spring of stiffness k = 300 N/m. When s = 0, the spring is compressed 50 mm. If the arm is pulled back such that s = 100 mm and released, determine the speed of the 0.3 kg pinball B just before the plunger strikes the stop, i.e., s = 0. Assume all sufaces of contact to be smooth. The ball moves in the horizontal plane. Note that the ball slides without rolling.
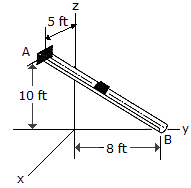
The block has a weight of 1.5 lb and slides along the smooth chute AB. It is released from rest at A, which has coordinates of A(5 ft, 0, 10 ft). Determine the speed at which it slides off at B, which has coordinates of B(0, 8 ft, 0).