Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
21.
In a circuit with capacitance connected to ac source, the rate of change of capacitor voltage is constant.
22.
Assertion (A): If Z1(s) and Z2(s) are positive real then Z1(s) + Z2(s) as well as 1/Z1(s) and 1/Z2(s) are positive real.
Reason (R): The poles of a positive real function are real or occur in conjugate pairs.
23.
A variable resistance R and capacitive reactance XC are connected in series. As R is varied, the locus of Z is
24.
The dual of a node is
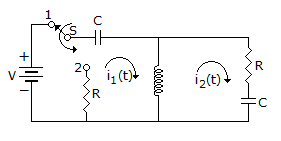
25.
At t = 0+, the current i1 is

Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers