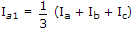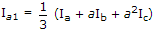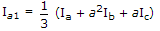Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
31.
A parallel resonant circuit can be used
32.
Which of the following theorems enables a number of voltage (or current) sources to be combined directly into a single voltage (or current) source?
33.
If Ia, Ib, Ic are line currents and Ia1 is the positive sequences component of Ia then
34.
If the numerator of Z(s) is one degree higher than denominator, Z(s) has a pole at infinity.
35.
An m derived low pass filter has fc = 1000 Hz, f∞ = 1250 Hz and m = 0.6. If m is increased, then
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers