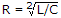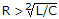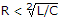Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
26.
A series RL circuit is switched on to an exponential source Ve-at at t = 0. The current 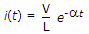
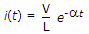
27.
A tie set schedule shows
28.
A constant k band stop filter has cutoff frequencies of 1000 and 4000 Hz. The attenuation will be maximum when frequency is
29.
The equation 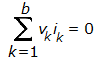 where v1, v2 ... vb are the instantaneous branch voltages and i1, i2 ... ib are the instantaneous branch currents pertains to
where v1, v2 ... vb are the instantaneous branch voltages and i1, i2 ... ib are the instantaneous branch currents pertains to
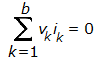 where v1, v2 ... vb are the instantaneous branch voltages and i1, i2 ... ib are the instantaneous branch currents pertains to
where v1, v2 ... vb are the instantaneous branch voltages and i1, i2 ... ib are the instantaneous branch currents pertains to30.
Transient current in an RLC circuit is oscillatory when
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers