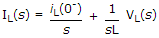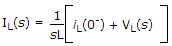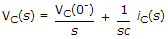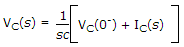Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
6.
Which one is correct option, if initial conditions is not zero, for inductor (L) and capacitor (c) is
7.
An RC impedance function has a constant value at s = 0. The last element in the first cauer synthesis
8.
Two port Z parameter not exist for the circuit if
9.
The current density J at a point and current I are related as 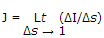
10.
For a reactance function H(s), the slope dH (jω)/dω is
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers