Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
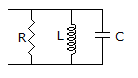
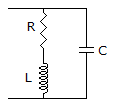
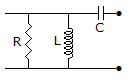
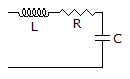
46.
The RLC circuit for driving point admittance function 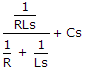 is
is
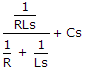 is
is47.
Assertion (A): A branch with no current through it can be replaced by an open circuit or short circuit.
Reason (R): Reciprocity theorem is applicable only if the circuit has one source.
48.
Three capacitors each 9 μF are connected in delta. The value of each capacitor in equivalent star connection is
49.
The function 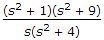 is
is
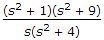 is
is50.
The electrolyte in nickel cadmium cell is dilute potassium hydroxide.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers