Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
46.
A system described by the following differential equation 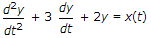 is initially rest for input x(t) = 2 u(t), the output y(t) is
is initially rest for input x(t) = 2 u(t), the output y(t) is
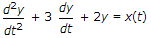 is initially rest for input x(t) = 2 u(t), the output y(t) is
is initially rest for input x(t) = 2 u(t), the output y(t) is47.
In a minimum function
48.
In a series circuit with fixed R and variable XL, the current locus lies in the fourth quadrant.
49.
A parallel connection of circuit is at below resonance circuit behave as
50.
Assertion (A): In figure the coefficients 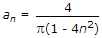 , n = 1, 2, ... and bn = 0
, n = 1, 2, ... and bn = 0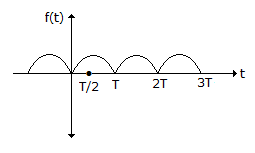
Reason (R): The periodic function is symmetrical about t = T and t = T/2.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers