Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis
Exercise : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
6.
The current wave in figure is passed through 3 H inductor. The voltage across inductance during the period 2 < t < 3 seconds is
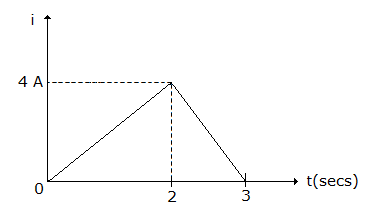

Answer: Option
Explanation:
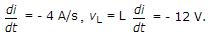
7.
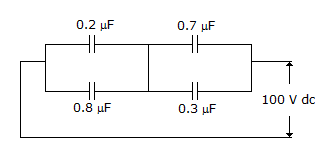
In figure, the charge on 0.8 μF capacitor is

Answer: Option
Explanation:
Each of parallel combination of capacitors is equal to 1 μF. Therefore, voltage across each capacitor is 50 V. Q = 0.8 x 50 = 40 μC.
8.
Maximum power transfer theorem finds application in
Answer: Option
Explanation:
In power and distribution circuits efficiency has to be very high.
9.
In a series L-C circuit fed by ac voltage, voltage drops across L and C are 40 V and 30 V respectively. The supply voltage is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
|V| = IXL - IXC.
10.
In a reactance function
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Only then the network has only L and C. If poles and zeros are not on jω axis, resistance will be there.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers