Electronics and Communication Engineering - Analog Electronics - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Analog Electronics - Section 1 (Q.No. 12)
12.
In figure, VEB = 0.6 V, β = 99. Then VC and IC are
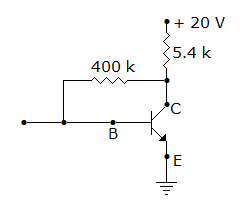

Answer: Option
Explanation:
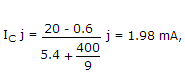
VC = 20 - 1.98 x 10-3 x 5.4 x 103  9.3 V.
9.3 V.
Discussion:
11 comments Page 2 of 2.
Nishad said:
5 years ago
We will apply for normal kvl.
First, understand that here feedback resistor is placed between collector and base to keep the transistor in active region irrespective of beta value
So current through 5.4k will be Ic+Ib. Current through 400k will be Ib.
Now apply kvl.
20 = 5.4k *(Ic+Ib) + 400k * Ib + Vbe.
Substitute Ic with beta*Ib.
We will get Ib = .02mA.
Now Ic =beta*Ib = 1.98mA.
Vc = Vcc- Rc( Ib + Ic)= 9.2V.
First, understand that here feedback resistor is placed between collector and base to keep the transistor in active region irrespective of beta value
So current through 5.4k will be Ic+Ib. Current through 400k will be Ib.
Now apply kvl.
20 = 5.4k *(Ic+Ib) + 400k * Ib + Vbe.
Substitute Ic with beta*Ib.
We will get Ib = .02mA.
Now Ic =beta*Ib = 1.98mA.
Vc = Vcc- Rc( Ib + Ic)= 9.2V.
(4)
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers