Electronics and Communication Engineering - Analog Electronics
Exercise : Analog Electronics - Section 7
- Analog Electronics - Section 11
- Analog Electronics - Section 21
- Analog Electronics - Section 20
- Analog Electronics - Section 19
- Analog Electronics - Section 18
- Analog Electronics - Section 17
- Analog Electronics - Section 16
- Analog Electronics - Section 15
- Analog Electronics - Section 14
- Analog Electronics - Section 13
- Analog Electronics - Section 12
- Analog Electronics - Section 1
- Analog Electronics - Section 10
- Analog Electronics - Section 9
- Analog Electronics - Section 8
- Analog Electronics - Section 7
- Analog Electronics - Section 6
- Analog Electronics - Section 5
- Analog Electronics - Section 4
- Analog Electronics - Section 3
- Analog Electronics - Section 2
41.
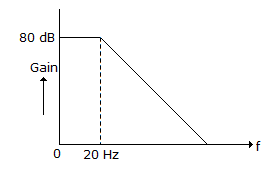
In figure gain bandwidth product is

42.
Consider the following statements
A totem pole configuration used in the output stage if an op-amp has the advantage of using
A totem pole configuration used in the output stage if an op-amp has the advantage of using
- Only n-p-n BJTs
- Complementary symmetrical pair of transistors
- Only one transistor
43.
Assertion (A): An op-amp amplifier can amplify dc signal
Reason (R): An op-amp amplifier is a direct coupled amplifier
44.
The most common method for biasing a JFET is
45.
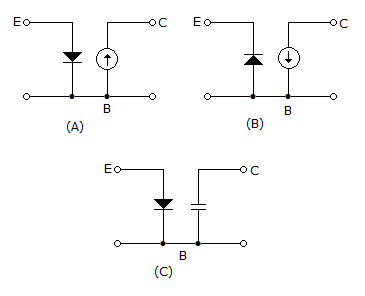
Which of the following figures is an ideal equivalent circuit of a n-p-n transistor?

Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers