Electronic Devices - DC Biasing-BJTs - Discussion
Discussion Forum : DC Biasing-BJTs - General Questions (Q.No. 20)
20.
Calculate ETh for this network.
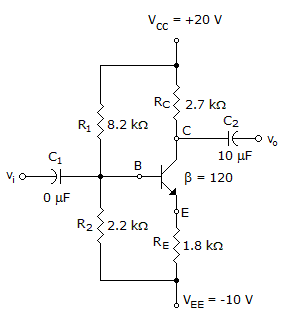
Discussion:
8 comments Page 1 of 1.
Severina said:
3 years ago
Using nodal Analysis:
Let Eth = B (for simplicity)
[(B-20)/8200 ]+ [(B +10)/ 2200) = 0.
B = -3.65 V * answer.
Let Eth = B (for simplicity)
[(B-20)/8200 ]+ [(B +10)/ 2200) = 0.
B = -3.65 V * answer.
Millize said:
4 years ago
Since βRE>>>10R2 ; 216k ohms >>> 22k ohms , approximate analysis can be used. Where Ib = 0, Ie=Ic & I1=I2 (R1&R2 in series). By KVL on left side, Vcc-I(R1+R2) +Vee = 0; I = (Vcc+Vee)/ (R1+R2) = 2.88 mA.
To get Eth it is usually the voltage drop in R2, but here the case is different since R2 is not connected to ground but is connected to a negative source, therefore, Eth = IR2+Vee is the total voltage drop on the R2 side.
Eth = (2.88mA)(2.2kohms)+ -10 =-3.65 V.
To get Eth it is usually the voltage drop in R2, but here the case is different since R2 is not connected to ground but is connected to a negative source, therefore, Eth = IR2+Vee is the total voltage drop on the R2 side.
Eth = (2.88mA)(2.2kohms)+ -10 =-3.65 V.
(3)
Reya said:
7 years ago
Vb = 20 - Ib(8200).
Also, Vb - Ib(2200) = -10 ------> Vb = -10 + Ib(2200).
20 - Ib(8200) = -10 + Ib(2200),
Ib = 2.8846mA,
Eth = Ib(R2) - VEE,
Eth = (2.88mA)(2200) - 10 = -3.6538 Volts.
Also, Vb - Ib(2200) = -10 ------> Vb = -10 + Ib(2200).
20 - Ib(8200) = -10 + Ib(2200),
Ib = 2.8846mA,
Eth = Ib(R2) - VEE,
Eth = (2.88mA)(2200) - 10 = -3.6538 Volts.
Aldrin said:
7 years ago
Here, we can use Vcc (R2/(R1+R2)) - 0.7.
(2)
Pure said:
9 years ago
Current I = (Vcc + Vee)/(R1 + R2),
Then Eth = IR2 - Vee.
Then Eth = IR2 - Vee.
Vincentio said:
9 years ago
The formula isn't R2 * Vcc/R1 + R2 = Eth?
If it is, how that the answer is C?
If it is, how that the answer is C?
Aniketh said:
10 years ago
Equivalent thevenin votage. But reference pts are not specified.
Curious Eng said:
10 years ago
What is E(Th)? anyone please?
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers