Digital Electronics - Counters
Exercise : Counters - General Questions
- Counters - General Questions
- Counters - True or False
- Counters - Filling the Blanks
71.
A 22-MHz clock signal is put into a MOD-16 counter. What is the frequency of the Q output of each stage of the counter?
72.
The designation 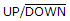 means that the ________.
means that the ________.
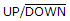 means that the ________.
means that the ________.73.
What type of device is shown below?

74.
Why can a synchronous counter operate at a higher frequency than a ripple counter?
75.
A multiplexed display being driven by a logic circuit:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers