Chemical Engineering - Chemical Reaction Engineering
Exercise : Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 2
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 1
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 2
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 3
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 4
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 5
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 6
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 7
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 8
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 9
- Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 10
21.
At a given temperature, K1, K2 and K3 are equilibrium constants for the following reactions 1, 2, 3 respectively.
CH4(g) + H2O(g) CO(g) + 3H2(g),
CO(g) + 3H2(g),
CO(g) + H2O(g) CO2(g) + H2(g)
CO2(g) + H2(g)
CH4(g) + 2H2O(g) CO2(g) + 4H2(g)
CO2(g) + 4H2(g)
Then K1, K2 and K3 are related as:
CH4(g) + H2O(g)
 CO(g) + 3H2(g),
CO(g) + 3H2(g), CO(g) + H2O(g)
 CO2(g) + H2(g)
CO2(g) + H2(g)CH4(g) + 2H2O(g)
 CO2(g) + 4H2(g)
CO2(g) + 4H2(g)Then K1, K2 and K3 are related as:
22.
In case of __________ reactions, the reaction rate does not decrease appreciably as the reaction proceeds.
23.
For nearly isothermal operation involving large reaction time in a liquid-phase reaction, the most suitable reactor is a __________ reactor.
24.
What is the Thiele modulus of the solid catalysed first order reaction, 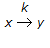 , if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ?
, if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ?
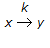 , if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ?
, if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ?25.
B.E.T. method can be used to determine the __________ of a porous catalyst.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers