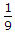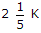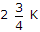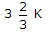Online Electronics and Communication Engineering Test - Previous Exam Papers Test 3
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
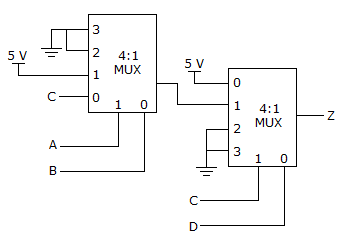
Output of first MUX = A(B + C)
Output of second MUX = C D + A B).
According to Gauss's law total flux leaving the closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by the closed surface
Qencl = (6 x 10-6) + (8 x 180 x 10-6) + (p x 42 x 25 x 10-9)
= (6 x 10-6) + (1.44 x 10-6) + (1.257 x 10-6)
= 8.697 μ Coulombs.
- sum of full adder
- carry of half adder
- difference of full subtractor
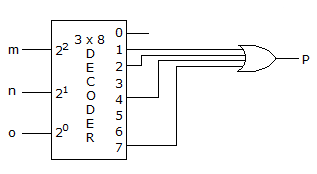
Let the two bits be A and B. Then the truth table be:
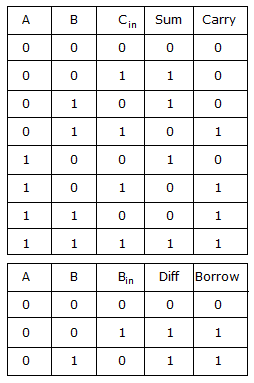
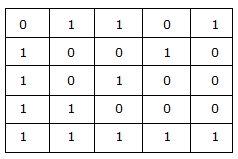
Now it is evident from the truth tables that Sum and Difference are same.
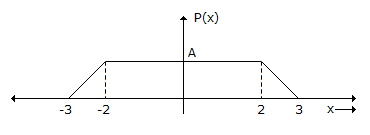
The mean of the distribution is:
Mean of the distribution = 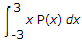
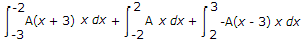
A = 1/5 then find mean.
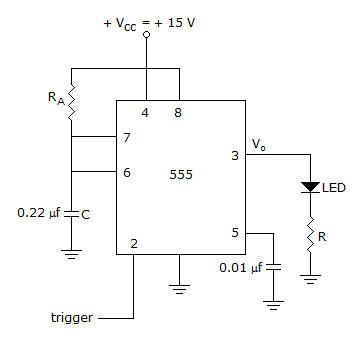
Timer operated in mono, mode
RAC =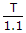
∴ RA = 41.4 KΩ
R = 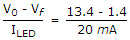 = 600 Ω.
= 600 Ω.
- E + F + G = LMN
- V + W = U . Z . Y . X . T
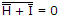 NAND B
NAND B- (UVW ⊕ WVU) = KJ(XY ⊕ XY)
Then f is equivalent to
(UVW ⊕ WVU) = 1 = KJ(XY ⊕ XY)
∴ KJ = 1
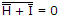 NAND B
NAND B
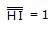
∴ HI = 1
Since f = GEF + 1 + LMON + TUVWXYZ = 1.
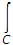 (4x3 + 10y4)
(4x3 + 10y4)
y = 2x
⇒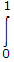 [4x3 + 10(2x)4]dx = 33
[4x3 + 10(2x)4]dx = 33
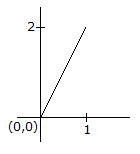
For a real skew symmetric matrix the non-zero eigen values are all pure imaginary and thus occurs in complex conjugate pair.
Y = P ⊕ Q ⊕ R, Z = RQ + P R + Q P

The circuit is a
Let P = 1101 Q = 1101
Yn = Pn ⊕ Qn ⊕ Rn
Z = Rn Qn + Pn Rn + Qn Pn
Constructing truth table

So that, Rn + 1 = Zn 1 ≥ n ≥ 3
Z4 = R5(MSB)
Hence, output is 00010 which show that it is a 4 bit subtractor giving P - Q.
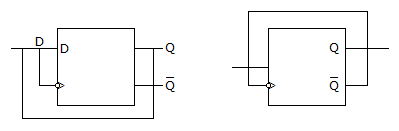
In both case input will always opposite to each other hence it is D FF.
 .
.
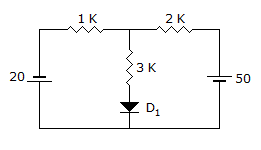
Diode is the non-linear element
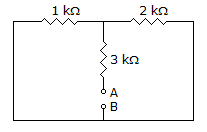
Find RTH across diode short voltage supplies.
RAB= RTH = 3K + (2K || 1K)
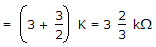 .
.
Assertion (A): The small signal analysis of a transistor amplifier is done to obtain the current gain, voltage gain and the conversion efficiency of an amplifier.
Reason (R): The small signal analysis of a transistor amplifier uses the small signal parameters of the transistor.
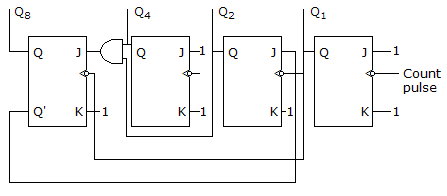
The count sequence of the above logic diagram is :
- Low heating of IC logic gates
- Compatibility with other logic gates
- Satisfactory and safe operation
- Standardization from IC manufacturing point of view.
- Full adder
- Full subtractor
- Half adder
- J-K flip-flop
- Counter