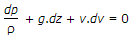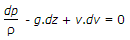Mechanical Engineering - Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Section 1 (Q.No. 18)
18.
Euler's equation in the differential form for the motion of liquids is given by
Discussion:
3 comments Page 1 of 1.
Muhammad Waqas said:
9 years ago
Bernoulli's equation is given by;
Energy per unit volume at point 1 = Energy per unit volume at point 2 = c.
Energy per unit volume at any point = c.
Pressure energy + potential energy per unit volume + Kinetic energy per unit volume = c.
P + ρgz + (1/2)ρ.v^2 = c.
P/ρ + gz + (1/2)v^2 = c.
Now differentiating the above equation.
dP/ρ + v.dv + g.dz = c.
Energy per unit volume at point 1 = Energy per unit volume at point 2 = c.
Energy per unit volume at any point = c.
Pressure energy + potential energy per unit volume + Kinetic energy per unit volume = c.
P + ρgz + (1/2)ρ.v^2 = c.
P/ρ + gz + (1/2)v^2 = c.
Now differentiating the above equation.
dP/ρ + v.dv + g.dz = c.
Dasthu said:
1 decade ago
pressure energy+kinetic energy+potential energy = const(newtons law by eliminating C.F ,S.T,V.F).
PV+(1/2)Mv^2+Mgh = c.
By diff it we get answer.
PV+(1/2)Mv^2+Mgh = c.
By diff it we get answer.
BENZ said:
9 years ago
Bernoulli's equation is:
P/ρ + V^2/2 + g*Z. Just differentiate it.
P/ρ + V^2/2 + g*Z. Just differentiate it.
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers