Engineering Mechanics - PKRB: Work and Energy
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Work and Energy"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Work and Energy" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Work and Energy"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "PKRB: Work and Energy" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "PKRB: Work and Energy" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "PKRB: Work and Energy" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Work and Energy" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "PKRB: Work and Energy" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "PKRB: Work and Energy"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "PKRB: Work and Energy" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- PKRB: Work and Energy - General Questions
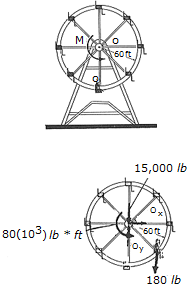
A man having a weight of 180 lb sits in a chair of the Ferris wheel, which has a weight of 15,000 lb and a radius of gyration of ko = 37 ft. If a torque of M = 80(103) lb • ft is applied about O, determine the angular velocity of the wheel after it has rotated 180°. Neglect the weight of the chairs and note that the man remains in an upright position as the wheel rotates. The wheel starts from rest in the position shown.
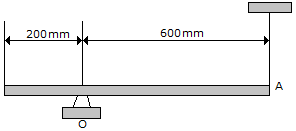
The uniform slender rod has a mass of 5 kg. Determine the magnitude of the reaction at the pin O when the cord at A is cut and  = 90°
= 90°
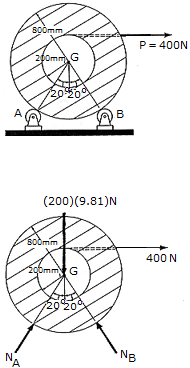
The spool of cable, originally at rest, has a mass of 200 kg and a radius of gyration of kG = 325 mm. If the spool rests on two small rollers A and B and a constant horizontal force of P = 400 N is applied to the end of the cable, compute the angular velocity of the spool when 8 m of cable has been unraveled. Neglect friction and the mass of the rollers and unraveled cable.
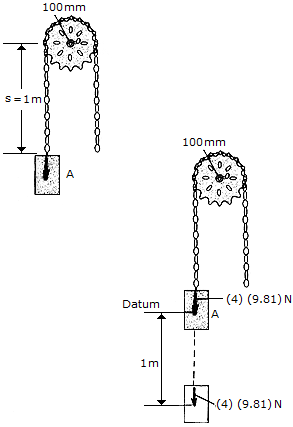
A chain that has a negligible mass is draped over a sprocket which has a mass of 2 kg and a radius of gyration of kO = 50 mm. If the 4-kg block A is released from rest in the position shown, s = 1 m, determine the angular velocity which the chain imparts th the sprocket when s = 2 m.

The beam having a weight of 150 lb is supported by two cables. If the cable at end B is cut so that the beam is released from rest when  = 30°, determine the speed at which end A strikes the wall. Neglect friction at B. Consider the beam to be a thin rod.
= 30°, determine the speed at which end A strikes the wall. Neglect friction at B. Consider the beam to be a thin rod.
 = 0.888 rad/s
= 0.888 rad/s