Engineering Mechanics - KOP: Force and Acceleration
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Force and Acceleration"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Force and Acceleration"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "KOP: Force and Acceleration"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "KOP: Force and Acceleration" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- KOP: Force and Acceleration - General Questions
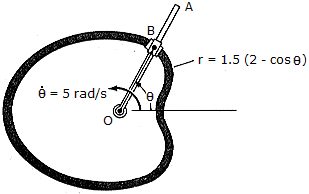
Rod OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular rate of 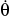 = 5 rad/s. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other slides over the horizontal curved rod, of which the shape is a limacon described by the equation r - 1.5(2 - cos
= 5 rad/s. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other slides over the horizontal curved rod, of which the shape is a limacon described by the equation r - 1.5(2 - cos  ) ft. If both collars weigh 0.75 lb, determine the normal force which the curved path exerts on one of the collars, and the force that OA exerts on the other collar at the instant
) ft. If both collars weigh 0.75 lb, determine the normal force which the curved path exerts on one of the collars, and the force that OA exerts on the other collar at the instant  = 90°.
= 90°.
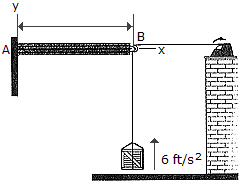
The 30-lb crate is being hoisted upward with a constant acceleration of 6 ft/s2. If the uniform beam AB has a weight of 200 lb, determine the components of reaction at A. Neglect the size and mass of the pulley at B.
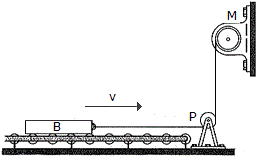
The 300-kg bar B, originally at rest, is being towed over a series of small rollers. Computer the force in the cable when t = 5s, if the motor M is drawing in the cable for a short time at a rate of v = (0.4t2) m/s, where t is in seconds (0  t
t  6 s). How far does the bar move in 5 s? Neglect the mass of the cable, pulley P, and the rollers.
6 s). How far does the bar move in 5 s? Neglect the mass of the cable, pulley P, and the rollers.

A 1.5-lb brick is released from rest A and slides down the inclined roof. If the coefficient of friction between the roof and the brick is  = 0.3, determine the speed at which the brick strikes the gutter G.
= 0.3, determine the speed at which the brick strikes the gutter G.

A ball having a mass of 2 kg slides without friction within a vertical circular slot. If it is released from rest when  = 10°, determine the force it exerts on the slot when it arrives at points A and B.
= 10°, determine the force it exerts on the slot when it arrives at points A and B.