Electronics - Inductors - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Inductors - General Questions (Q.No. 36)
36.
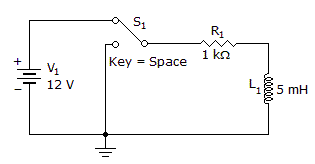
How long until the current is at a maximum?

Discussion:
8 comments Page 1 of 1.
Syed Shakeeb said:
4 years ago
5*RC is the time constant required the capacitor to fully charge.
Pritam said:
6 years ago
Please someone explain why we are not using 5*RC?
Khalid said:
1 decade ago
It must be 25 micro sec, because the current to be maximum it must take 5T.
So L/R = 5us then multiply with 5. The answer will be 25 micro sec.
So L/R = 5us then multiply with 5. The answer will be 25 micro sec.
Guest said:
1 decade ago
What happened to 5Tc before max current achieved?
Jagadeesh said:
1 decade ago
Since the circuit given is an energized RL circuit and max. current flows in that particular circuit.
And that max. current flow time depends on the circuit elements such as Resistor and Inductor.
Therefore according to network theory the time constant is given by, T=L/R.
And that max. current flow time depends on the circuit elements such as Resistor and Inductor.
Therefore according to network theory the time constant is given by, T=L/R.
YayyaY said:
1 decade ago
Time constants in electrical circuits
In an RL circuit composed of a single resistor and inductor, the time constant Ï„ (in seconds) is
where R is the resistance (in ohms) and L is the inductance (in henries).
Similarly, in an RC circuit composed of a single resistor and capacitor, the time constant Ï„ (in seconds) is:
where R is the resistance (in ohms) and C is the capacitance (in farads).
[from wiki]
In an RL circuit composed of a single resistor and inductor, the time constant Ï„ (in seconds) is
where R is the resistance (in ohms) and L is the inductance (in henries).
Similarly, in an RC circuit composed of a single resistor and capacitor, the time constant Ï„ (in seconds) is:
where R is the resistance (in ohms) and C is the capacitance (in farads).
[from wiki]
Muhammad Sohaib said:
1 decade ago
Please explain again.
Samrat said:
1 decade ago
Time constant = L/R = 5 mH/1 KOhm = 5 us
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers
 s
s