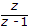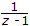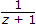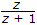Electronics and Communication Engineering - Signals and Systems
Exercise : Signals and Systems - Section 3
- Signals and Systems - Section 1
- Signals and Systems - Section 2
- Signals and Systems - Section 3
- Signals and Systems - Section 4
- Signals and Systems - Section 5
- Signals and Systems - Section 6
- Signals and Systems - Section 7
- Signals and Systems - Section 8
- Signals and Systems - Section 9
- Signals and Systems - Section 10
31.
A signal is sampled at Nyquist rate fs = 2f0. The function can be recovered from its samples only. If it is a
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Nyqist theorem is defined with respect to sinusoidal signal.
32.
A voltage wave is v = 50 sin ωt. Its average value calculated over full one cycle is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Average of sinusoid over full cycle is zero.
33.
If f1 (t) and f2 (f) are two functions of time and a and b are constants, then
Answer: Option
Explanation:
£f(t) = 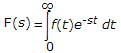
£-1F(s) = f(t)
£[a f1(t) + bf2(t)] = aF1(s) + bF2(s)
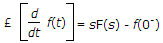
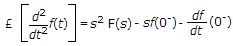
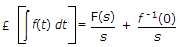
where 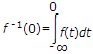
£[f(t - T)] = e-sT F(s)
£[e-at f(t)] = F(s + a)
Initial value theorem 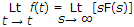
Final value theroem 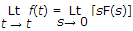
Convolution Integral 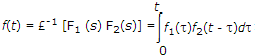
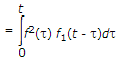
where t is dummy variable for t.
34.
The z transform of x(n) = ∪(n)
Answer: Option
Explanation:
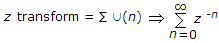
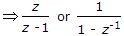 .
.
35.
Fourier transform of f(t) =
Answer: Option
Explanation:
It is differentiational Property of F.T. 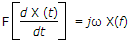 .
.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers