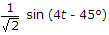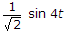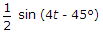Electronics and Communication Engineering - Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1 (Q.No. 36)
36.
A series RL circuit has 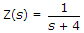 . If a voltage 4 sint + 4t is applied, the steady state current will be
. If a voltage 4 sint + 4t is applied, the steady state current will be
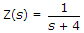 . If a voltage 4 sint + 4t is applied, the steady state current will be
. If a voltage 4 sint + 4t is applied, the steady state current will beAnswer: Option
Explanation:
R = 4 Ω, L = 1 H, ω = 4 rad/sec, XL = 4 Ω
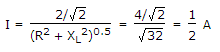
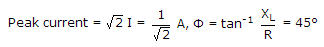
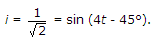
Discussion:
6 comments Page 1 of 1.
RAVI said:
8 years ago
Please, someone, explain it clearly.
Hannah said:
8 years ago
How did they get the value of omega?
Preeti said:
9 years ago
Here z(s) = R + SL eqauting this to given z(s) how it becomes R = 4 L = 1?
Manoja said:
10 years ago
Series RL circuit:
Vl(s) is voltage across inductor.
Vl(s) = (Ls/(R + Ls))Vin(s).
Vr(s) is voltage across resistor.
Vr(s) =(R/(R + Ls))Vin(s).
The current in the circuit is the same everywhere since the circuit is in series:
I(s) = Vin(s)/(R + Ls).
Hl(s) = (Ls/(R + Ls)).
Hr(s) = (R/(R + Ls)).
Common pole:
s = -R/L.
Given s = -4.
So, R = 4 ohm, L = 1H.
Vl(s) is voltage across inductor.
Vl(s) = (Ls/(R + Ls))Vin(s).
Vr(s) is voltage across resistor.
Vr(s) =(R/(R + Ls))Vin(s).
The current in the circuit is the same everywhere since the circuit is in series:
I(s) = Vin(s)/(R + Ls).
Hl(s) = (Ls/(R + Ls)).
Hr(s) = (R/(R + Ls)).
Common pole:
s = -R/L.
Given s = -4.
So, R = 4 ohm, L = 1H.
Bhumika said:
1 decade ago
How L = 1 and R = 4 Ω?
Wasim said:
1 decade ago
L = 1 How?
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers