Digital Electronics - Interfacing to the Analog World
Exercise : Interfacing to the Analog World - Filling the Blanks
- Interfacing to the Analog World - General Questions
- Interfacing to the Analog World - True or False
- Interfacing to the Analog World - Filling the Blanks
11.
A counter-ramp ADC uses a comparator to compare the input voltage with ________.
12.
A binary-weighter resistor DAC is practical only up to a resolution of ________.
13.
A simultaneous A/D converter is also known as a(n) ________ A/D converter.
14.
The figure given below represents a ________.
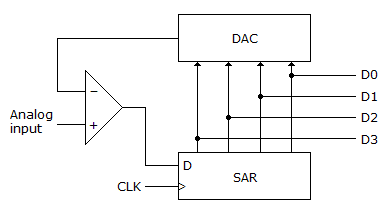
15.
The primary disadvantage of the simultaneous A/D converter is ________.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers