Digital Electronics - Interfacing to the Analog World
Exercise : Interfacing to the Analog World - General Questions
- Interfacing to the Analog World - General Questions
- Interfacing to the Analog World - True or False
- Interfacing to the Analog World - Filling the Blanks
16.
The basic approach to testing D/A converters is to:
17.
What is the maximum output voltage for the circuit shown below?
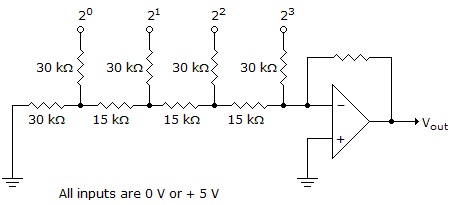
18.
One major difference between a counter-ramp A/D converter and a successive-approximation converter is:
19.
Which of the following characterizes an analog quantity?
20.
What is the resolution of a D/A converter?
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers